Caspase-11 stimulates rapid flagellin-independent pyroptosis in response to Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 23307811
- PMCID: PMC3562791
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211521110
Caspase-11 stimulates rapid flagellin-independent pyroptosis in response to Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
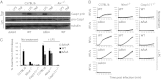
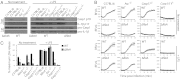
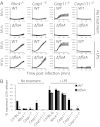
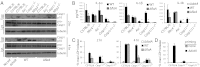
A flagellin-independent caspase-1 activation pathway that does not require NAIP5 or NRLC4 is induced by the intracellular pathogen Legionella pneumophila. Here we demonstrate that this pathway requires caspase-11. Treatment of macrophages with LPS up-regulated the host components required for this caspase-11 activation pathway. Activation by Legionella differed from caspase-11 activation using previously described agonists in that Legionella caspase-11 activation was rapid and required bacteria with a functional type IV secretion system called Dot/Icm. Legionella activation of caspase-11 induced pyroptosis by a mechanism independent of the NAIP/NLRC4 and caspase-1 axis. Legionella activation of caspase-11 stimulated activation of caspase-1 through NLRP3 and ASC. Induction of caspase-11-dependent responses occurred in macrophages deficient in the adapter proteins TRIF or MyD88 but not in macrophages deficient in both signaling factors. Although caspase-11 was produced in macrophages deficient in the type-I IFN receptor, there was a severe defect in caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis in these cells. These data indicate that macrophages respond to microbial signatures to produce proteins that mediate a capsase-11 response and that the caspase-11 system provides an alternative pathway for rapid detection of an intracellular pathogen capable of evading the canonical caspase-1 activation system that responds to bacterial flagellin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Caspase-11: the noncanonical guardian of cytosolic sanctity.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Mar 13;13(3):243-5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.02.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23498948
References
-
- Shin S, Roy CR. Host cell processes that influence the intracellular survival of Legionella pneumophila. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10(6):1209–1220. - PubMed
-
- Amer A, et al. Regulation of Legionella phagosome maturation and infection through flagellin and host Ipaf. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(46):35217–35223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

