Nicotine induces inhibitor of differentiation-1 in a Src-dependent pathway promoting metastasis and chemoresistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 23308043
- PMCID: PMC3540937
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.121044
Nicotine induces inhibitor of differentiation-1 in a Src-dependent pathway promoting metastasis and chemoresistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Abstract
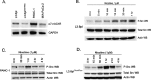
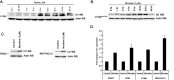
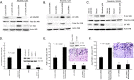
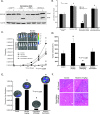
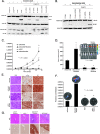
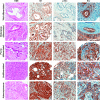
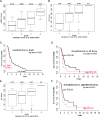
Smoking is a significant risk factor for pancreatic cancer, but the molecular mechanisms by which tobacco smoke components promote the growth and progression of these cancers are not fully understood. While nicotine, the addictive component of tobacco smoke, is not a carcinogen, it has been shown to promote the growth of non-small cell lung and pancreatic cancers in a receptor-dependent fashion. Here, we show that stimulation of pancreatic cancer cells with nicotine concentrations that are within the range of human exposure results in activation of Src kinase, which facilitated the induction of the inhibitor of differentiation-1 (Id1) transcription factor. Depletion of Id1 prevented nicotine-mediated induction of proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells, indicating that it is a major mediator of nicotine function. Nicotine could promote the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancers orthotopically implanted into SCID mice; in addition, cells stably expressing a short hairpin RNA for Id1 did not grow or metastasize in response to nicotine. Nicotine could also confer resistance to apoptosis induced by gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and depletion of Src or Id1 rendered the cells sensitive to gemcitabine. Further, nicotine could effectively inhibit the chemotherapeutic effects of gemcitabine on pancreatic tumors xenografted into mice. Clinical analyses of resected pancreatic cancer specimens demonstrated a statistically significant correlation between Id1 expression and phospho-Src, tumor grade/differentiation, and worsening overall patient survival. These results demonstrate that exposure to tobacco smoke components might promote pancreatic cancer progression, metastasis, and chemoresistance and highlight the role of Id1 in these processes.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–236. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Li Y, Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Ali S, Abbruzzese JL, Gallick GE, Sarkar FH. Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells is linked with activation of the notch signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2400–2407. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Azmi AS, Kong D, Sarkar FH. Pancreatic cancer: understanding and overcoming chemoresistance. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:27–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
