Overexpression of the AtSHI gene in poinsettia, Euphorbia pulcherrima, results in compact plants
- PMID: 23308204
- PMCID: PMC3538768
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053377
Overexpression of the AtSHI gene in poinsettia, Euphorbia pulcherrima, results in compact plants
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(7). doi:10.1371/annotation/010f6c7f-9745-4810-a370-c96fb1f583e9
Abstract
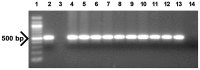
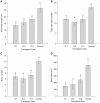
Euphorbia pulcherrima, poinsettia, is a non-food and non-feed vegetatively propagated ornamental plant. Appropriate plant height is one of the most important traits in poinsettia production and is commonly achieved by application of chemical growth retardants. To produce compact poinsettia plants with desirable height and reduce the utilization of growth retardants, the Arabidopsis SHORT INTERNODE (AtSHI) gene controlled by the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter was introduced into poinsettia by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Three independent transgenic lines were produced and stable integration of transgene was verified by PCR and Southern blot analysis. Reduced plant height (21-52%) and internode lengths (31-49%) were obtained in the transgenic lines compared to control plants. This correlates positively with the AtSHI transcript levels, with the highest levels in the most dwarfed transgenic line (TL1). The indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) content appeared lower (11-31% reduction) in the transgenic lines compared to the wild type (WT) controls, with the lowest level (31% reduction) in TL1. Total internode numbers, bract numbers and bract area were significantly reduced in all transgenic lines in comparison with the WT controls. Only TL1 showed significantly lower plant diameter, total leaf area and total dry weight, whereas none of the AtSHI expressing lines showed altered timing of flower initiation, cyathia abscission or bract necrosis. This study demonstrated that introduction of the AtSHI gene into poinsettia by genetic engineering can be an effective approach in controlling plant height without negatively affecting flowering time. This can help to reduce or avoid the use of toxic growth retardants of environmental and human health concern. This is the first report that AtSHI gene was overexpressed in poinsettia and transgenic poinsettia plants with compact growth were produced.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of poinsettia, Euphorbia pulcherrima, with virus-derived hairpin RNA constructs confers resistance to Poinsettia mosaic virus.Plant Cell Rep. 2008 Jun;27(6):1027-38. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0526-9. Epub 2008 Mar 8. Plant Cell Rep. 2008. PMID: 18327592 Free PMC article.
-
Production of compact plants by overexpression of AtSHI in the ornamental Kalanchoë.Plant Biotechnol J. 2010 Feb;8(2):211-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009.00478.x. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Plant Biotechnol J. 2010. PMID: 20051037
-
Poinsettia (Euphorbia pulcherrima Willd. ex Klotzsch).Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1224:347-56. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1658-0_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25416270
-
Anthocyanin metabolic engineering of Euphorbia pulcherrima: advances and perspectives.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 15;14:1176701. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1176701. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37255565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dawn of Plant Molecular Biology: How Three Key Methodologies Paved the Way.Curr Protoc. 2022 Apr;2(4):e417. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.417. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35441802 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Shi-Related Sequence Family and Functional Identification of GmSRS18 Involving in Drought and Salt Stresses in Soybean.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 6;21(5):1810. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051810. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32155727 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the SRS Gene Family in Cucurbitaceae: Clade Identification and Expression Analysis of CmSRS Genes Under Drought and Salt Stress.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jul 20;14(7):891. doi: 10.3390/biology14070891. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723448 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, structural analysis and expression profiles of short internodes related sequence gene family in quinoa.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 22;13:961925. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.961925. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36072673 Free PMC article.
-
Genome biology of the paleotetraploid perennial biomass crop Miscanthus.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 28;11(1):5442. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18923-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33116128 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Kalanchoë blossfeldiana, Containing Individual rol Genes and Open Reading Frames Under 35S Promoter, Exhibit Compact Habit, Reduced Plant Growth, and Altered Ethylene Tolerance in Flowers.Front Plant Sci. 2021 May 7;12:672023. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.672023. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34025708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandler S, Tanaka Y (2007) Genetic modification in floriculture. Crit Rev Plant Sci 26: 169–197.
-
- Lütken H, Clarke JL, Müller R (2012) Genetic engineering and sustainable production of ornamentals: current status and future directions. Plant Cell Rep 31: 1141–11573. - PubMed
-
- Ascough G, Erwin J, Van Staden J (2008) Biotechnology and ornamental horticulture. South Afr J Bot 74: 357.
-
- Müller R (2011) Physiology and genetics of plant quality improvement. PhD Thesis, University of Copenhagen.
-
- Ecke IP, Faust JE, Higgins A, Williams J (2004) The Ecke Poinsettia Manual. Ball Publishing, Illinois. 1–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

