A global transcriptome analysis reveals molecular hallmarks of neural stem cell death, survival, and differentiation in response to partial FGF-2 and EGF deprivation
- PMID: 23308259
- PMCID: PMC3538603
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053594
A global transcriptome analysis reveals molecular hallmarks of neural stem cell death, survival, and differentiation in response to partial FGF-2 and EGF deprivation
Abstract
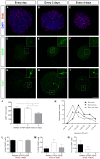
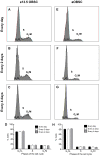
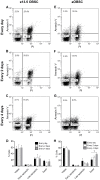
Neurosphere cell culture is a commonly used model to study the properties and potential applications of neural stem cells (NSCs). However, standard protocols to culture NSCs have yet to be established, and the mechanisms underlying NSC survival and maintenance of their undifferentiated state, in response to the growth factors FGF-2 and EGF are not fully understood. Using cultures of embryonic and adult olfactory bulb stem cells (eOBSCs and aOBSCs), we analyzed the consequences of FGF-2 and EGF addition at different intervals on proliferation, cell cycle progression, cell death and differentiation, as well as on global gene expression. As opposed to cultures supplemented daily, addition of FGF-2 and EGF every 4 days significantly reduced the neurosphere volume and the total number of cells in the spheres, mainly due to increased cell death. Moreover, partial FGF-2 and EGF deprivation produced an increase in OBSC differentiation during the proliferative phase. These changes were more evident in aOBSC than eOBSC cultures. Remarkably, these effects were accompanied by a significant upregulation in the expression of endogenous Fgf-2 and genes involved in cell death and survival (Cryab), lipid catabolic processes (Pla2g7), cell adhesion (Dscaml1), cell differentiation (Dscaml1, Gpr17, S100b, Ndrg2) and signal transduction (Gpr17, Ndrg2). These findings support that a daily supply of FGF-2 and EGF is critical to maintain the viability and the undifferentiated state of NSCs in culture, and they reveal novel molecular hallmarks of NSC death, survival and the initiation of differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I is necessary for neural stem cell proliferation and demonstrates distinct actions of epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):7194-202. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07194.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549730 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of Nonproliferating Astrocytes into Neurogenic Neural Stem Cells: Control by FGF2 and Interferon-γ.Stem Cells. 2016 Dec;34(12):2861-2874. doi: 10.1002/stem.2483. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 27603577
-
Pax6 is essential for the maintenance and multi-lineage differentiation of neural stem cells, and for neuronal incorporation into the adult olfactory bulb.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Dec 1;23(23):2813-30. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0058. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 25117830 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetic analysis of FGFR1 signalling reveals distinct roles of MAPK and PLCgamma1 activation for self-renewal of adult neural stem cells.Mol Brain. 2009 Jun 8;2:16. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-2-16. Mol Brain. 2009. PMID: 19505325 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation Anesthetics Play a Janus-Faced Role in Self-Renewal and Differentiation of Stem Cells.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 18;14(9):1167. doi: 10.3390/biom14091167. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
p66Shc deletion confers apoptotic resistance to loss of EGFR-ERK signalling in neural stem cells.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):479. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07778-8. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40593476 Free PMC article.
-
Identify Down syndrome transcriptome associations using integrative analysis of microarray database and correlation-interaction network.Hum Genomics. 2018 Jan 19;12(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40246-018-0133-y. Hum Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29351810 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of FGF2-dependent mRNA: microRNA networks during lens fiber cell differentiation.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Dec 9;3(12):2239-55. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.008698. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 24142921 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of chemo- and radio-resistant phenotypes with the gap junction, adhesion and extracellular matrix in a three-dimensional culture model of soft sarcoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 10;34(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0175-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26055407 Free PMC article.
-
An Efficient Method for Generating Murine Hypothalamic Neurospheres for the Study of Regional Neural Progenitor Biology.Endocrinology. 2020 Apr 1;161(4):bqaa035. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa035. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32154873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB, McKay RD (1990) CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell 60: 585–595. - PubMed
-
- Malatesta P, Hartfuss E, Gotz M (2000) Isolation of radial glial cells by fluorescent-activated cell sorting reveals a neuronal lineage. Development 127: 5253–5263. - PubMed
-
- Noctor SC, Flint AC, Weissman TA, Dammerman RS, Kriegstein AR (2001) Neurons derived from radial glial cells establish radial units in neocortex. Nature 409: 714–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

