The potent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) entry inhibitor HR212 blocks formation of the envelope glycoprotein gp41 six-helix bundle
- PMID: 23308369
- PMCID: PMC3581026
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2012.0059
The potent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) entry inhibitor HR212 blocks formation of the envelope glycoprotein gp41 six-helix bundle
Abstract
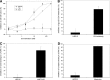
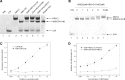
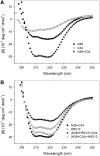
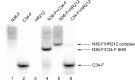
HR212, a recombinant protein composed of the heptad repeat, is a rationally designed human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) fusion inhibitor. This protein can be easily produced by Escherichia coli at a low cost. Previously, studies indicated that HR212 can efficiently inhibit the entry and replication of both laboratory and clinical HIV-1 strains, and this protein is more stable and less sensitive to proteinases than T20. The procedure of HIV-1 entry into the host cells can be divided into three main steps: gp120-CD4 interactions, coreceptor binding, and gp41 six-helix bundle formation and subsequent membrane fusion. The present study demonstrates that HR212 does not block gp120-CD4 binding or interfere with binding to the coreceptors CXCR4 and CCR5. Instead, HR212 efficiently blocks the six-helix bundle formation between peptides derived from the N-terminal heptad repeat (NHR) and the C-terminal heptad repeat (CHR) region of gp41. Fluorescence native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (FN-PAGE) indicated that HR212 could form a complex with peptide N36 to block gp41 fusogenic core formation. These results suggest that HR212 inhibits HIV-1 entry by targeting the NHR region of gp41. Therefore, HR212 can potentially be developed as a novel, high-efficiency, specific HIV-1 entry inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ADS-J1 inhibits HIV-1 infection and membrane fusion by targeting the highly conserved pocket in the gp41 NHR-trimer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1838(5):1296-305. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.12.022. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24388952
-
Identification of a human protein-derived HIV-1 fusion inhibitor targeting the gp41 fusion core structure.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e66156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066156. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741527 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 variants with a single-point mutation in the gp41 pocket region exhibiting different susceptibility to HIV fusion inhibitors with pocket- or membrane-binding domain.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Dec;1818(12):2950-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.07.020. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22867851
-
High throughput screening and characterization of HIV-1 entry inhibitors targeting gp41: theories and techniques.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(15):1827-43. doi: 10.2174/1381612043384466. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15180543 Review.
-
HIV-1 gp41 fusion intermediate: a target for HIV therapeutics.J Formos Med Assoc. 2010 Feb;109(2):94-105. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(10)60029-0. J Formos Med Assoc. 2010. PMID: 20206833 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Apr;23(2):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.03.007. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23602427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan C. Liu S. Jiang S. HIV-1 gp41 fusion intermediate: A target for HIV therapeutics. J Formos Med Assoc. 2010;109(2):94–105. - PubMed
-
- He Y. Xiao Y. Song H, et al. Design and evaluation of sifuvirtide, a novel HIV-1 fusion inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(17):11126–11134. - PubMed
-
- Wyatt R. Sodroski J. The HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins: Fusogens, antigens, and immunogens. Science. 1998;280(5371):1884–1888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

