Platelet-derived growth factor-induced Akt phosphorylation requires mTOR/Rictor and phospholipase C-γ1, whereas S6 phosphorylation depends on mTOR/Raptor and phospholipase D
- PMID: 23311350
- PMCID: PMC3560233
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-3
Platelet-derived growth factor-induced Akt phosphorylation requires mTOR/Rictor and phospholipase C-γ1, whereas S6 phosphorylation depends on mTOR/Raptor and phospholipase D
Abstract
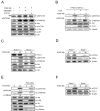
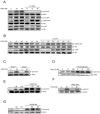
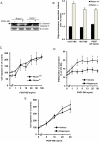
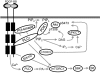
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) can be found in two multi-protein complexes, i.e. mTORC1 (containing Raptor) and mTORC2 (containing Rictor). Here, we investigated the mechanisms by which mTORC1 and mTORC2 are activated and their downstream targets in response to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB treatment. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibited PDGF-BB activation of both mTORC1 and mTORC2. We found that in Rictor-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts, or after prolonged rapamycin treatment of NIH3T3 cells, PDGF-BB was not able to promote phosphorylation of Ser473 in the serine/threonine kinase Akt, whereas Thr308 phosphorylation was less affected, suggesting that Ser473 in Akt is phosphorylated in an mTORC2-dependent manner. This reduction in Akt phosphorylation did not influence the phosphorylation of the S6 protein, a well established protein downstream of mTORC1. Consistently, triciribine, an inhibitor of the Akt pathway, suppressed PDGF-BB-induced Akt phosphorylation without having any effect on S6 phosphorylation. Thus, mTORC2 does not appear to be upstream of mTORC1. We could also demonstrate that in Rictor-null cells the phosphorylation of phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) and protein kinase C (PKC) was impaired, and the PKCα protein levels strongly reduced. Furthermore, interfering with the PLCγ/Ca2+/PKC pathway inhibited PDGF-BB-induced Akt phosphorylation. In addition, PDGF-BB-induced activation of mTORC1, as measured by phosphorylation of the downstream S6 protein, was dependent on phospholipase D (PLD). It has been shown that Erk1/2 MAP-kinase directly phosphorylates and activates mTORC1; in partial agreement with this finding, we found that a Mek1/2 inhibitor delayed S6 phosphorylation in response to PDGF-BB, but it did not block it. Thus, whereas both mTORC1 and mTORC2 are activated in a PI3K-dependent manner, different additional signaling pathways are needed. mTORC1 is activated in a PLD-dependent manner and promotes phosphorylation of the S6 protein, whereas mTORC2, in concert with PLCγ signaling, promotes Akt phosphorylation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
mTORC1-activated S6K1 phosphorylates Rictor on threonine 1135 and regulates mTORC2 signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;30(4):908-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00601-09. Epub 2009 Dec 7. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19995915 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in regulation of glioblastoma multiforme growth and motility.Int J Oncol. 2009 Oct;35(4):731-40. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000386. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19724909
-
Raptor-rictor axis in TGFbeta-induced protein synthesis.Cell Signal. 2008 Feb;20(2):409-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.10.027. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18068336
-
Diverse signaling mechanisms of mTOR complexes: mTORC1 and mTORC2 in forming a formidable relationship.Adv Biol Regul. 2019 May;72:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Adv Biol Regul. 2019. PMID: 31010692 Review.
-
RES-529: a PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitor that dissociates the mTORC1 and mTORC2 complexes.Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Jul;27(6):475-87. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000354. Anticancer Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26918392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The phosphatidylethanolamine derivative diDCP-LA-PE mimics intracellular insulin signaling.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 2;6:27267. doi: 10.1038/srep27267. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27251941 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women.Science. 2021 Jun 11;372(6547):1224-1229. doi: 10.1126/science.abe9985. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Science. 2021. PMID: 33888596 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genomic clustering analysis identifies molecular subtypes of thymic epithelial tumors independent of World Health Organization histologic type.Oncotarget. 2021 Jun 8;12(12):1178-1186. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27978. eCollection 2021 Jun 8. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34136086 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced menin expression impairs rapamycin effects as evidenced by an increase in mTORC2 signaling and cell migration.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Oct 1;16(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0278-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30285764 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases Cγ1 contributes to extracellular matrix synthesis of human osteoarthritis chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 28;15(8):13236-46. doi: 10.3390/ijms150813236. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25073093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heldin CH, Westermark B. Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1283–1316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

