Propofol protects against high glucose-induced endothelial adhesion molecules expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 23311470
- PMCID: PMC3579710
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-13
Propofol protects against high glucose-induced endothelial adhesion molecules expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Hyperglycemia could induce oxidative stress, activate transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), up-regulate expression of endothelial adhesion molecules, and lead to endothelial injury. Studies have indicated that propofol could attenuate oxidative stress and suppress NF-κB activation in some situations. In the present study, we examined whether and how propofol improved high glucose-induced up-regulation of endothelial adhesion molecules in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
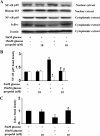
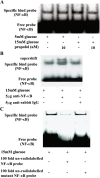
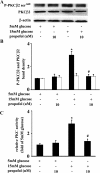
Methods: Protein expression of endothelial adhesion molecules, NF-κB, inhibitory subunit of NF-κBα (IκBα), protein kinase Cβ2 (PKCβ2), and phosphorylation of PKCβ2 (Ser(660)) were measured by Western blot. NF-κB activity was measured by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. PKC activity was measured with SignaTECT PKC assay system. Superoxide anion (O(2)(.-)) accumulation was measured with the reduction of ferricytochrome c assay. Human peripheral mononuclear cells were prepared with Histopaque-1077 solution.
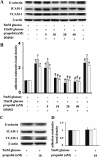
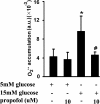
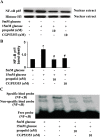
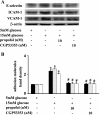
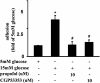
Results: High glucose induced the expression of endothelial selectin (E-selectin), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and increased mononuclear-endothelial adhesion. High glucose induced O(2)(.-) accumulation, PKCβ2 phosphorylation and PKC activation. Further, high glucose decreased IκBα expression in cytoplasm, increased the translocation of NF-κB from cytoplasm to nuclear, and induced NF-κB activation. Importantly, we found these high glucose-mediated effects were attenuated by propofol pretreatment. Moreover, CGP53353, a selective PKCβ2 inhibitor, decreased high glucose-induced NF-κB activation, adhesion molecules expression, and mononuclear-endothelial adhesion.
Conclusion: Propofol, via decreasing O(2)(.-) accumulation, down-regulating PKCβ2 Ser(660) phosphorylation and PKC as well as NF-κB activity, attenuated high glucose-induced endothelial adhesion molecules expression and mononuclear-endothelial adhesion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ketamine attenuates high-glucose-mediated endothelial inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;98(3):156-161. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2019-0185. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32078386
-
Propofol ameliorates endothelial inflammation induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Role of phosphatase A2.Vascul Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;73:149-57. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26070526
-
Propofol protects against high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Anesth Analg. 2012 Feb;114(2):303-9. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31823f0c42. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22156331
-
Essential Oil from Fructus Alpiniae Zerumbet Protects Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells In Vitro from Injury Induced by High Glucose Levels by Suppressing Nuclear Transcription Factor-Kappa B Signaling.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Oct 4;23:4760-4767. doi: 10.12659/msm.906463. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28976943 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of protein kinase Cbeta2 prevents acute effects of high glucose on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells.Circulation. 2004 Jul 6;110(1):91-6. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000133384.38551.A8. Epub 2004 Jun 21. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15210597
Cited by
-
Ethyl Rosmarinate Protects High Glucose-Induced Injury in Human Endothelial Cells.Molecules. 2018 Dec 19;23(12):3372. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123372. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30572638 Free PMC article.
-
High Glucose Induces Endothelial COX2 and iNOS Expression via Inhibition of Monomethyltransferase SETD8 Expression.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Feb 23;2020:2308520. doi: 10.1155/2020/2308520. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32185234 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 participates in redox-sensitive leukocyte recruitment triggered by methylglyoxal.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Sep 30;13:134. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0134-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 25270604 Free PMC article.
-
Vaspin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation and adhesion molecule expression via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular endothelial cells.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Feb 12;13:41. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-13-41. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 24517399 Free PMC article.
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in arginase-II-mediated eNOS-uncoupling in obesity.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Jul 18;13:113. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0113-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 25034973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morigi M, Angioletti S, Imberti B, Donadelli R, Micheletti G, Figliuzzi M, Remuzzi A, Zoja C, Remuzzi G. Leukocyte-endothelial interaction is augmented by high glucose concentrations and hyperglycemia in a NF-kB-dependent fashion. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:1905–1915. doi: 10.1172/JCI656. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

