Allograft outcomes in outbred mice
- PMID: 23311531
- PMCID: PMC3582712
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12056
Allograft outcomes in outbred mice
Abstract
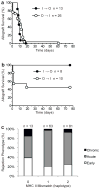
Inbreeding depression and lack of genetic diversity in inbred mice could mask unappreciated causes of graft failure or remove barriers to tolerance induction. To test these possibilities, we performed heart transplantation between outbred or inbred mice. Unlike untreated inbred mice in which all allografts were rejected acutely (6-16 days posttransplantation), untreated outbred mice had heterogeneous outcomes, with grafts failing early (<4 days posttransplantation), acutely (6-24 days) or undergoing chronic rejection (>75 days). Blocking T cell costimulation induced long-term graft acceptance in both inbred and outbred mice, but did not prevent the early graft failure observed in the latter. Further investigation of this early phenotype established that it is dependent on the donor, and not the recipient, being outbred and that it is characterized by hemorrhagic necrosis and neutrophilic vasculitis in the graft without preformed, high titer antidonor antibodies in the recipient. Complement or neutrophil depletion prevented early failure of outbred grafts, whereas transplanting CD73-deficient inbred hearts, which are highly susceptible to ischemia-reperfusion injury, recapitulated the early phenotype. Therefore, outbred mice could provide broader insight into donor and recipient determinants of allograft outcomes but their hybrid vigor and genetic diversity do not constitute a uniform barrier to tolerance induction.
© Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures




References
-
- Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D. The genetic basis of inbreeding depression. Genet Res. 1999;74:329–340. - PubMed
-
- Frankham R. Conservation genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:305–327. - PubMed
-
- Beck JA, Lloyd S, Hafezparast M, Lennon-Pierce M, Eppig JT, Festing MF, et al. Genealogies of mouse inbred strains. Nat Genet. 2000;24:23–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

