Glycogen storage disease type Ia: linkage of glucose, glycogen, lactic acid, triglyceride, and uric acid metabolism
- PMID: 23312056
- PMCID: PMC3812663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2012.08.005
Glycogen storage disease type Ia: linkage of glucose, glycogen, lactic acid, triglyceride, and uric acid metabolism
Abstract
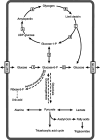
A female presented in infancy with hypotonia, undetectable serum glucose, lactic acidosis, and triglycerides >5000 mg/dL. The diagnosis of type 1A glycogen storage disease was made via the result of a liver biopsy, which showed increased glycogen and absent glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme activity. The patient was treated with dextrose administered orally, which was replaced by frequent feedings of cornstarch, which resulted in an improvement of her metabolic parameters. At age 18 years of age, she had marked hypertriglyceridemia (3860 mg/dL) and eruptive xanthomas and was treated with fenofibrate, atorvastatin, and fish oil. At age 29 years she was noted to have multiple liver adenomas, severe anemia, and hyperuricemia. Aggressive cornstarch therapy was commenced with a goal of maintaining her blood glucose levels >75 mg/dL and lactate levels <2 mmol/L. After 15 months on this regimen, her lipids levels (measured in mg/dL) off all medications were as follows: total cholesterol 222, triglycerides 179, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol 32, and calculated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol 154. Her weight was stable with a body mass index of 24.8 kg/m(2). Her liver adenomas had decreased in size, and her anemia and hyperuricemia had improved. She was homozygous for the R83C missense mutation in G6PC. Our data indicate that optimized metabolic control to maintain blood glucose levels >75 mg/dL is critical in the management of this disease.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fenofibrate rapidly decreases hepatic lipid and glycogen storage in neonatal mice with glycogen storage disease type Ia.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jan 15;29(2):286-294. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz290. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 31816064 Free PMC article.
-
Improvements of hypertriglyceridemia and hyperlacticemia in Japanese children with glycogen storage disease type Ia by medium-chain triglyceride milk.Eur J Pediatr. 2007 Oct;166(10):1009-16. doi: 10.1007/s00431-006-0372-0. Epub 2007 Jan 6. Eur J Pediatr. 2007. PMID: 17206455
-
Impaired Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein catabolism links hypoglycemia to hypertriglyceridemia in Glycogen Storage Disease type Ia.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 Jul;44(4):879-892. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12380. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 33739445 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition therapy for hepatic glycogen storage diseases.J Am Diet Assoc. 1993 Dec;93(12):1423-30. doi: 10.1016/0002-8223(93)92246-t. J Am Diet Assoc. 1993. PMID: 8245377 Review.
-
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011 May 20;6:27. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-6-27. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011. PMID: 21599942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatic glucose sensing and integrative pathways in the liver.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Apr;71(8):1453-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1505-z. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24196749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Genetics of Dyslipidemias and Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 12;17(4):659. doi: 10.3390/nu17040659. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40004987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of mRNA Therapeutics for the Treatment of Hepatic Diseases.Mol Ther. 2019 Apr 10;27(4):794-802. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.12.012. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30655211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term complications of glycogen storage disease type Ia in the canine model treated with gene replacement therapy.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018 Nov;41(6):965-976. doi: 10.1007/s10545-018-0223-y. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018. PMID: 30043186 Free PMC article.
-
A Liver-Specific Thyromimetic, VK2809, Decreases Hepatosteatosis in Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia.Thyroid. 2019 Aug;29(8):1158-1167. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0007. Thyroid. 2019. PMID: 31337282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ingelsson E, Schaefer EJ, Contois JH, McNamara JR, Sullivan L, Keyes MJ, Pencina MJ, Schoonmaker C, Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Vasan RS. Clinical utilty of different lipid measures for prediction of coronary heart disease in men and women. JAMA. 2007;298:776–785. - PubMed
-
- Asztalos BF, Cupples LA, Demissie S, Horvath KV, Cox CE, Batista MC, Schaefer EJ. High-density lipoprotein subpopulation profile and coronary heart disease prevalence in male participants in the Framingham Offspring Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:2181–2187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

