Antinociceptive activities of lidocaine and the nav1.8 blocker a803467 in diabetic rats
- PMID: 23312086
- PMCID: PMC3447446
Antinociceptive activities of lidocaine and the nav1.8 blocker a803467 in diabetic rats
Abstract
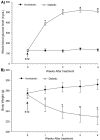
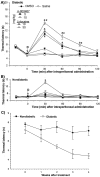
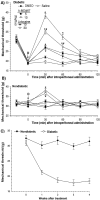
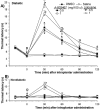
The streptozocin-induced diabetic rat is a model of chronic pain that shows signs of hyperalgesia and allodynia and may replicate signs in diabetic humans. Here we investigated the antinociceptive effects of A803467, a highly selective blocker of Nav1.8 channels, in diabetic rats with painful neuropathy. We systemically (intraperitoneal) or locally (intraplantar) administered A803467 (or lidocaine, a nonselective sodium channel blocker, as a control) to diabetic rats with hyperalgesia and allodynia and then measured thermal latencies and mechanical thresholds. With intraperitoneal administration, A803467 led to 6-fold greater reduction of hyperalgesia and 2-fold greater reduction of allodynia than did lidocaine. Whereas the antihyperalgesic effects of lidocaine and A803467 were similar after intraplantar administration, A803467 (1 mg) was at least 2 times more effective as an antiallodynic than was lidocaine (0.5 mg). These results suggest that compared with lidocaine, systemic or local blockade of Nav1.8 channels by A803467 may more effectively relieve hyperalgesia and allodynia in diabetic neuropathy.
Figures
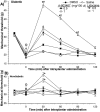
References
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN. 1999. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci 2:541–548 - PubMed
-
- Amaya F, Decosterd I, Samad TA, Plumpton C, Tate S, Mannion RJ, Costigan M, Woolf CJ. 2000. Diversity of expression of the sensory-neuron-specific TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium-ion channels SNS and SNS2. Mol Cell Neurosci 15:331–342 - PubMed
-
- Andriambeloson E, Baillet C, Vitte PA, Garotta G, Dreano M, Callizot N. 2006. Interleukin-6 attenuates the development of experimental diabetes-related neuropathy. Neuropathology 26:32–42 - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. 2007. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:451–465 - PubMed
-
- Berkley KJ. 1997. Sex differences in pain. Behav Brain Sci 20:371–380 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
