Neocortical somatostatin-expressing GABAergic interneurons disinhibit the thalamorecipient layer 4
- PMID: 23312523
- PMCID: PMC3556168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.11.004
Neocortical somatostatin-expressing GABAergic interneurons disinhibit the thalamorecipient layer 4
Abstract
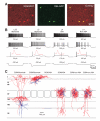
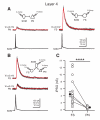
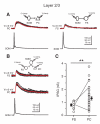
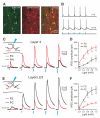
Subtypes of GABAergic interneurons (INs) are crucial for cortical function, yet their specific roles are largely unknown. In contrast to supra- and infragranular layers, where most somatostatin-expressing (SOM) INs are layer 1-targeting Martinotti cells, the axons of SOM INs in layer 4 of somatosensory cortex largely remain within layer 4. Moreover, we found that whereas layers 2/3 SOM INs target mainly pyramidal cells (PCs), layer 4 SOM INs target mainly fast-spiking (FS) INs. Accordingly, optogenetic inhibition of SOM INs in an active cortical network increases the firing of layers 2/3 PCs whereas it decreases the firing of layer 4 principal neurons (PNs). This unexpected effect of SOM INs on layer 4 PNs occurs via their inhibition of local FS INs. These results reveal a disinhibitory microcircuit in the thalamorecipient layer through interactions among subtypes of INs and suggest that the SOM IN-mediated disinhibition represents an important circuit mechanism for cortical information processing.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
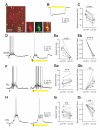
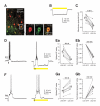
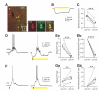
References
-
- Agmon A, Connors BW. Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience. 1991;41:365–379. - PubMed
-
- Beierlein M, Gibson JR, Connors BW. Two dynamically distinct inhibitory networks in layer 4 of the neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2003;90:2987–3000. - PubMed
-
- Bruno RM, Sakmann B. Cortex is driven by weak but synchronously active thalamocortical synapses. Science. 2006;312:1622–1627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

