Initiation of antiretroviral therapy before 6 months of age is associated with faster growth recovery in South African children perinatally infected with human immunodeficiency virus
- PMID: 23312691
- PMCID: PMC3640753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.11.025
Initiation of antiretroviral therapy before 6 months of age is associated with faster growth recovery in South African children perinatally infected with human immunodeficiency virus
Abstract
Objective: To describe the effects of age at antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation on growth outcomes among children infected with HIV followed for 48 months after treatment initiation.
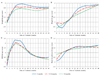
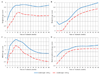
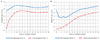
Study design: This secondary analysis describes anthropometric changes in children infected with HIV in Johannesburg, South Africa who initiated ritonavir-boosted lopinavir-based ART before 24 months of age and were randomized to continue ritonavir-boosted lopinavir or to receive nevirapine after achieving and maintaining virologic suppression. Weight, height, and head circumference were measured at visits over 48 months post-ART initiation. Growth patterns including weight-for-age z-scores (WAZs), height-for-age z-scores, body mass index-for-age z-scores, and head circumference for age z-score were compared between children initiating ART<6 months, 6-12 months, and 12-24 months of age.
Results: A total of 195 children (mean±SD age 10.7±5.9 months), including 54 (27.7%)<6 months, 69 (35.4%) 6-12 months, and 72 (36.9%) 12-24 months of age at ART initiation, were evaluated. In the first 12 months on treatment, children<6 months of age at ART initiation experienced more rapid improvement in WAZ (1.98 vs 1.44, P=.084) and head circumference for age z-score (1.24 vs 0.45, P=.004) than children who initiated ART between 12-24 months of age. By 48 months on ART, growth outcomes were similar, regardless of age at ART initiation. WAZ approached population norms by 12 months on ART. Although improving, height-for-age z-scores remained on average 1.0 z-score below population norms at 48 months of therapy.
Conclusions: Initiation of ART before 6 months of age results in more rapid growth recovery in children infected with HIV. These data provide further evidence for the importance of prompt diagnosis and early initiation of ART for infants infected with HIV.
Copyright © 2013 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bobat R, Coovadia H, Moodley D, Coutsoudis A, Gouws E. Growth in early childhood in a cohort of children born to HIV-1-infected women from Durban, South Africa. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2001;21:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Moye J, Jr, Rich KC, Kalish LA, Sheon AR, Diaz C, Cooper ER, et al. Natural history of somatic growth in infants born to women infected by human immunodeficiency virus. Women and Infants Transmission Study Group. J Pediatr. 1996;128:58–69. - PubMed
-
- Henderson R, Miotti P, Saavedra J, Dallabetta G, Chiphangwi J, Liomba G, et al. Longitudinal growth during the first 2 years of life in children born to HIV-infected mothers in Malawi, Africa. Pediatr AIDS HIV Infect. 1996;7:91. - PubMed
-
- Berhane R, Bagenda D, Marum L, Aceng E, Ndugwa C, Bosch RJ, et al. Growth failure as a prognostic indicator of mortality in pediatric HIV infection. Pediatrics. 1997;100:E7. - PubMed
-
- Buchacz K, Cervia JS, Lindsey JC, Hughes MD, Seage GR, 3rd, Dankner WM, et al. Impact of protease inhibitor-containing combination antiretroviral therapies on height and weight growth in HIV-infected children. Pediatrics. 2001;108:E72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

