Posaconazole as rescue therapy in African histoplasmosis
- PMID: 23312726
- PMCID: PMC9427377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2012.06.027
Posaconazole as rescue therapy in African histoplasmosis
Abstract
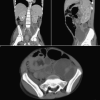
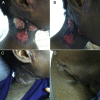
African histoplasmosis is a granulomatous mycosis caused by Histoplasma capsulatum var. duboisii. Treatment is usually extrapolated from guidelines for classical histoplasmosis, and includes 2-4 weeks of amphotericin B followed by a step-down maintenance therapy with itraconazole. Pediatric usage of posaconazole, an oral second-generation azole, remains off-label, but recent surveys show that it is safe and well tolerated in children. We report a case of disseminated African histoplasmosis in a 12-year-old boy from Guinea-Bissau. Therapy with amphotericin B and itraconazole led to a progressive clinical deterioration. A dramatic and lasting improvement was observed using posaconazole. He completed 12 months of therapy. No relapse was noted during or 3 months after treatment. We report that posaconazole may be a safe and efficacious drug in the salvage management of disseminated AH, either in patients with disease refractory to conventional anti-fungal therapy, or in patients whose serious adverse effects of first-line drugs preclude its use.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wheat L.J. Histoplasmosis: a review from clinicians from non-endemic areas. Mycoses. 2006;49:274–282. - PubMed
-
- Manfredi R., Mazzoni A., Nanetti A., Chiodo F. Histoplasmosis capsulate and duboisii in Europe: the impact of the HIV pandemic, travel and immigration. Eur J Epidemiol. 1994;10:675–681. - PubMed
-
- Gugnani H.C., Muotoe-Okafor F. African histoplasmosis: a review. Rev Iberoam Micol. 1997;14:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Wheat L.J., Freifeld A.G., Kleiman M.B., et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with histoplasmosis: 2007 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:807–825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

