The five Rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore
- PMID: 23312823
- PMCID: PMC3667973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.11.005
The five Rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore
Abstract
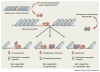
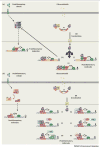
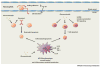
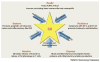
Glucocorticoids are essential for maintaining homeostasis and regulate a wide variety of physiological processes. Therapeutically, synthetic glucocorticoids are widely prescribed for the treatment of inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and malignancies of lymphoid origin. In this review we examine emerging evidence highlighting both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids on both the innate and adaptive immune systems. We incorporate these findings into the more traditional anti-inflammatory role attributed to glucocorticoids, and propose how the two seemingly disparate processes seamlessly work together to resolve cellular responses to inflammatory stimuli. These ideas provide a framework by which glucocorticoids ready and reinforce the innate immune system, and repress the adaptive immune system, to help to resolve inflammation and restore homeostasis.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Nathan C, Ding A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:871–882. - PubMed
-
- Clark AR, Belvisi MG. Maps and legends: the quest for dissociated ligands of the glucocorticoid receptor. Pharmacol Ther. 2012;134:54–67. - PubMed
-
- Cole TJ, et al. Targeted disruption of the glucocorticoid receptor gene blocks adrenergic chromaffin cell development and severely retards lung maturation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1608–1621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

