VZV multifocal vasculopathy with ischemic optic neuropathy, acute retinal necrosis and temporal artery infection in the absence of zoster rash
- PMID: 23312850
- PMCID: PMC3586992
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2012.12.021
VZV multifocal vasculopathy with ischemic optic neuropathy, acute retinal necrosis and temporal artery infection in the absence of zoster rash
Abstract
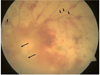
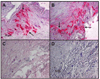
We describe a 54-year-old diabetic woman who developed ischemic optic neuropathy followed by acute retinal necrosis and multiple areas of focal venous beading. Vitreous fluid contained amplifiable VZV DNA but not HSV-1, CMV or toxoplasma DNA. The clinical presentation was remarkable for jaw claudication and intermittent scalp pain, prompting a temporal artery biopsy that was pathologically negative for giant cell arteritis, but notable for VZV antigen. The current case adds to the clinical spectrum of multifocal VZV vasculopathy. The development of acute VZV retinal necrosis after ischemic optic neuropathy supports the notion that vasculitis is an important additional mechanism in the development of VZV retinal injury.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nordborg C, Nordborg E, Petursdottir V, LaGuardia J, Mahalingam R, Wellish M, et al. Search for VZV in giant cell arteritis. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:413–414. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy PG, Grinfeld E, Esiri MM. Absence of detection of varicella-zoster virus DNA in temporal artery biopsies obtained from patients with giant cell arteritis. J Neurol Sci. 2003;215:27–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

