Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma in celiac disease: a large retrospective study
- PMID: 23313469
- PMCID: PMC7185558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2012.12.001
Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma in celiac disease: a large retrospective study
Abstract
Introduction: Prognosis of enteropathy-associated T cell lymphoma is poor but predictors of survival remain ill-defined. How clinical presentation, pathological features and therapies influence outcome was evaluated in 37 thoroughly characterized patients with celiac disease and T-cell lymphoma.
Patients and methods: Medical files were studied retrospectively. Lymphoma and intestinal mucosa were analysed by histopathology, multiplex PCR and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes phenotyping. Survival and prognostic factors were analysed using Kaplan-Meier curves with Logrank test and Cox Model.
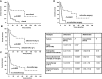
Results: Lymphoma complicated non clonal enteropathy, celiac disease (n=15) and type I refractory celiac disease (n=2) in 17 patients and clonal type II refractory celiac disease in 20 patients. Twenty-five patients underwent surgery with resection of the main tumour mass in 22 cases. In univariate analysis, non clonal celiac disease, serum albumin level>21.6g/L at diagnosis, chemotherapy and surgical resection predicted good survival (p=0.0007, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, respectively). In multivariate analysis, serum albumin level>21.6g/L, chemotherapy and reductive surgery were all significantly associated with increased survival (p<0.002, p<0.03, p<0.03, respectively).
Conclusions: Our study underlines the prognostic value of celiac disease type in patients with T-cell lymphoma, and suggests that a combination of nutritional, chemotherapy and reductive surgery may improve survival.
Copyright © 2013 Editrice Gastroenterologica Italiana S.r.l. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Novakovic B.J., Novakovic S., Frkovic-Grazio S. A single-center report on clinical features and treatment response in patients with intestinal T cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Oncology Reports. 2006;16:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Egan L.J., Walsh S.V., Stevens F.M. Celiac-associated lymphoma. A single institution experience of 30 cases in the combination chemotherapy era. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 1995;21:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Daum S., Ullrich R., Heise W. Intestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a multicenter prospective clinical study from the German study group on intestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2003;21:2740–2746. - PubMed
-
- Gale J., Simmonds P.D., Mead G.M. Enteropathy-type intestinal t-cell lymphoma: clinical features and treatment of 31 patients in a single center. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2000;18:795–803. - PubMed
-
- Cellier C., Delabesse E., Helmer C. Refractory sprue, coeliac disease, and enteropathy-associated t-cell lymphoma. French coeliac disease study group. Lancet. 2000;356:203–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

