Detoxification of aldehydes by histidine-containing dipeptides: from chemistry to clinical implications
- PMID: 23313711
- PMCID: PMC4418549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.12.017
Detoxification of aldehydes by histidine-containing dipeptides: from chemistry to clinical implications
Abstract
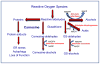
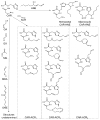
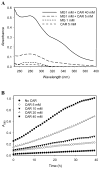
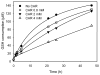
Aldehydes are generated by oxidized lipids and carbohydrates at increased levels under conditions of metabolic imbalance and oxidative stress during atherosclerosis, myocardial and cerebral ischemia, diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases and trauma. In most tissues, aldehydes are detoxified by oxidoreductases that catalyze the oxidation or the reduction of aldehydes or enzymatic and nonenzymatic conjugation with low molecular weight thiols and amines, such as glutathione and histidine dipeptides. Histidine dipeptides are present in micromolar to millimolar range in the tissues of vertebrates, where they are involved in a variety of physiological functions such as pH buffering, metal chelation, oxidant and aldehyde scavenging. Histidine dipeptides such as carnosine form Michael adducts with lipid-derived unsaturated aldehydes, and react with carbohydrate-derived oxo- and hydroxy-aldehydes forming products of unknown structure. Although these peptides react with electrophilic molecules at lower rate than glutathione, they can protect glutathione from modification by oxidant and they may be important for aldehyde quenching in glutathione-depleted cells or extracellular space where glutathione is scarce. Consistent with in vitro findings, treatment with carnosine has been shown to diminish ischemic injury, improve glucose control, ameliorate the development of complications in animal models of diabetes and obesity, promote wound healing and decrease atherosclerosis. The protective effects of carnosine have been linked to its anti-oxidant properties, its ability to promote glycolysis, detoxify reactive aldehydes and enhance histamine levels. Thus, treatment with carnosine and related histidine dipeptides may be a promising strategy for the prevention and treatment of diseases associated with high carbonyl load.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carnosine and related dipeptides as quenchers of reactive carbonyl species: from structural studies to therapeutic perspectives.Biofactors. 2005;24(1-4):77-87. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520240109. Biofactors. 2005. PMID: 16403966
-
Detoxification of cytotoxic alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes by carnosine: characterization of conjugated adducts by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and detection by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry in rat skeletal muscle.J Mass Spectrom. 2002 Dec;37(12):1219-28. doi: 10.1002/jms.381. J Mass Spectrom. 2002. PMID: 12489081
-
Imidazole dipeptides can quench toxic 4-oxo-2(E)-nonenal: Molecular mechanism and mass spectrometric characterization of the reaction products.J Pept Sci. 2018 Aug;24(8-9):e3097. doi: 10.1002/psc.3097. Epub 2018 Jul 3. J Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 29971858
-
Biochemical, Biomedical and Metabolic Aspects of Imidazole-Containing Dipeptides with the Inherent Complexity to Neurodegenerative Diseases and Various States of Mental Well-Being: A Challenging Correction and Neurotherapeutic Pharmaceutical Biotechnology for Treating Cognitive Deficits, Depression and Intellectual Disabilities.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(8):738-78. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666140827104918. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25158972 Review.
-
Carnosine: its properties, functions and potential therapeutic applications.Mol Aspects Med. 1992;13(5):379-444. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(92)90006-l. Mol Aspects Med. 1992. PMID: 9765790 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of amino acid and nucleotide metabolism by crustacean hyperglycemic hormone in the muscle and hepatopancreas of the crayfish Procambarus clarkia.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 26;14(12):e0221745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221745. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31877133 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Hummingbirds and Chickens Provides Mechanistic Insight on the Histidine Containing Dipeptide Role in Skeletal Muscle Metabolism.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 3;8(1):14788. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32636-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30283073 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lipoxidation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 18;11:621938. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.621938. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33679605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lewis acid-driven self-assembly of diiridium macrocyclic catalysts imparts substrate selectivity and glutathione tolerance.Chem Sci. 2023 Sep 4;14(37):10264-10272. doi: 10.1039/d3sc02836d. eCollection 2023 Sep 27. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37772092 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Cerebroprotective Potential of d- and l-Carnosine Following Ischemic Stroke in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 26;21(9):3053. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093053. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32357505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11:81–128. - PubMed
-
- De Zwart LL, Meerman JHN, Commandeur JNM, Vermeulen NPE. Biomarkers of free radical damage applications in experimental animals and in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999;26:202–226. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Ho CT. Flavour chemistry of methylglyoxal and glyoxal. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:4140–4149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

