The combination of sorafenib and radiation preferentially inhibits breast cancer stem cells by suppressing HIF-1α expression
- PMID: 23314174
- PMCID: PMC3597559
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2013.2228
The combination of sorafenib and radiation preferentially inhibits breast cancer stem cells by suppressing HIF-1α expression
Abstract
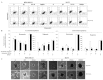
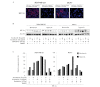
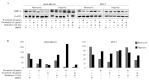
The importance of anticancer stem cell research for breast cancer lies in the possibility of providing new approaches for an improved understanding of anticancer activity and cancer treatment. In this study, we demonstrated that the preclinical therapeutic efficacy of combining the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib with radiation was more effective in hypoxia-exposed breast cancer stem cells. We assessed cell viability and Annexin V to evaluate the combined effect of sorafenib and radiation following exposure to hypoxia. Our results showed that the synergistic cytotoxicity increased tumor cell apoptosis significantly and reduced cell proliferation in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells under hypoxic conditions compared to sorafenib or radiation alone in vitro. Additionally, the combined treatment induced G2/M cell cycle arrest. Notably, the combination of sorafenib and radiation eliminated CD44+CD24-/low cells preferentially, which highly expressed hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and effectively inhibited primary and secondary mammosphere formation in MDA-MB-231 cells. A combined effect on MDA-MB‑231 cells in response to hypoxia was shown by inhibiting angiogenesis and metastasis by suppression of HIF-1α and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2). Collectively, these results indicate that the efficacy of sorafenib combined with radiation for treating human breast cancer cells is synergistic and suggest a new therapeutic approach to prevent breast cancer progression by eliminating breast cancer stem cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sorafenib blocks the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway, inhibits tumor invasion, and induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells.DNA Cell Biol. 2014 May;33(5):275-81. doi: 10.1089/dna.2013.2184. Epub 2014 Mar 10. DNA Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24611881
-
Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by EF24 through Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-dependent HIF-1α inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1847-57. doi: 10.1002/hep.26224. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299930
-
MiR-338-3p inhibits hepatocarcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib by targeting hypoxia-induced factor 1α.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 22;9(12):e115565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115565. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25531114 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor effects of dauricine on sorafenib-treated human lung cancer cell lines via modulation of HIF-1α signaling pathways.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 10;42(5):157. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02679-4. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40205002 Free PMC article.
-
2-Methoxyestradiol synergizes with sorafenib to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma by simultaneously dysregulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and -2.Cancer Lett. 2014 Dec 1;355(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25218350
Cited by
-
Effects of hypoxia on human cancer cell line chemosensitivity.BMC Cancer. 2013 Jul 5;13:331. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-331. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23829203 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting signaling pathways of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 as a potential target in the treatment of breast cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Mar;47(3):2061-2071. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05306-9. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32072404
-
Diagnostic value of elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging and strain ratio for breast tumors.J Breast Cancer. 2014 Mar;17(1):76-82. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2014.17.1.76. Epub 2014 Mar 28. J Breast Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24744801 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Induced Cancer Cell Responses Driving Radioresistance of Hypoxic Tumors: Approaches to Targeting and Radiosensitizing.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 4;13(5):1102. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051102. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel cancer treatment paradigm targeting hypoxia-induced factor in conjunction with current therapies to overcome resistance.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 18;42(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02724-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37460927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cell, cancer and cancer stem cell. Nature. 2001;414:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Generali D, Buffa FM, Berruti A, et al. Phosphorylated ERalpha, HIF-1alpha, and MAPK signaling as predictors of primary endocrine treatment response and resistance in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:227–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

