Systems biology approaches to identify developmental bases for lung diseases
- PMID: 23314295
- PMCID: PMC3615902
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2013.7
Systems biology approaches to identify developmental bases for lung diseases
Abstract
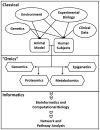
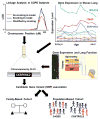
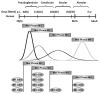
A greater understanding of the regulatory processes contributing to lung development could be helpful to identify strategies to ameliorate morbidity and mortality in premature infants and to identify individuals at risk for congenital and/or chronic lung diseases. Over the past decade, genomics technologies have enabled the production of rich gene expression databases providing information for all genes across developmental time or in diseased tissue. These data sets facilitate systems biology approaches for identifying underlying biological modules and programs contributing to the complex processes of normal development and those that may be associated with disease states. The next decade will undoubtedly see rapid and significant advances in redefining both lung development and disease at the systems level.
Figures
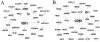
References
-
- Bhattacharya S, Mariani TJ. Array of hope: expression profiling identifies disease biomarkers and mechanism. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37:855–862. - PubMed
-
- Snoep JL, Bruggeman F, Olivier BG, Westerhoff HV. Towards building the silicon cell: a modular approach. Biosystems. 2006;83:207–216. - PubMed
-
- Hood L, Rowen L, Galas DJ, Aitchison JD. Systems biology at the Institute for Systems Biology. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2008;7:239–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

