New insight into the mechanisms underlying the function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic β-cells: the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway effector β-catenin
- PMID: 23314611
- PMCID: PMC3605164
- DOI: 10.4161/isl.23345
New insight into the mechanisms underlying the function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic β-cells: the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway effector β-catenin
Abstract
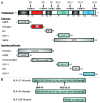
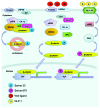
During the past two decades, the exploration of function of two incretin hormones, namely glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP), has led to the development of two categories of novel therapeutic agents for diabetes and its complications, known as GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists and DPP-IV inhibitors. Mechanisms underlying the function of GLP-1, however, still need to be further explored. GLP-1 not only functions as an incretin hormone in stimulating insulin secretion in response to nutritional, hormonal and neuronal stimulations, but also acts as an "insulin-like" factor in β-cell and extra-pancreatic organs. In addition to these insulinotropic and insulinomimetic effects, GLP-1 was shown to exert its protective effect in β-cell by repressing the expression of TxNIP, a mediator of glucolipotoxicity. A number of recent studies have shown that the Wnt signaling pathway effector, the bipartite transcription factor β-catenin/TCF, controls not only the production of GLP-1, but also the function of GLP-1. Furthermore, previously assumed "degradation" products of GLP-1(7-36)amide, including GLP-1(9-36)amide and GLP-1(28-36)amide, have been shown to exert beneficial effect in pancreas and extra-pancreatic tissues or cell lineages. Here we summarized our current knowledge on the metabolic, proliferative and protective effects of GLP-1(7-36)amide and its cleavage fragments, mainly focusing on pancreatic β-cells and the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway effector β-catenin.
Keywords: GLP-1; TCF7L2; TxNIP; Wnt signaling pathway; β-catenin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review.
-
Two incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP: comparison of their actions in insulin secretion and β cell preservation.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;107(2):248-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21820006 Review.
-
The role of the Wnt signaling pathway in incretin hormone production and function.Front Physiol. 2012 Jul 12;3:273. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00273. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22934027 Free PMC article.
-
Incretin action in the pancreas: potential promise, possible perils, and pathological pitfalls.Diabetes. 2013 Oct;62(10):3316-23. doi: 10.2337/db13-0822. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23818527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel extrapancreatic effects of incretin.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):76-9. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12495. Epub 2016 Mar 31. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GLP-1(28-36)amide, a Long Ignored Peptide Revisited.Open Biochem J. 2014 Dec 31;8:107-11. doi: 10.2174/1874091X01408010107. eCollection 2014. Open Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25598850 Free PMC article.
-
Acarbose: safe and effective for lowering postprandial hyperglycaemia and improving cardiovascular outcomes.Open Heart. 2015 Oct 19;2(1):e000327. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2015-000327. eCollection 2015. Open Heart. 2015. PMID: 26512331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic function of glucagon-like peptide-1 and its based diabetes drugs.Med Rev (2021). 2024 Jun 4;4(4):312-325. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0018. eCollection 2024 Aug. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39135602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-inflammatory feature of glucagon-like peptide-1 and its based diabetes drugs-Therapeutic potential exploration in lung injury.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Nov;12(11):4040-4055. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36386481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Contributions of Wnt Signaling: More Than Controlling Flight.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 9;9:709823. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.709823. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
