Visuomotor discordance during visually-guided hand movement in virtual reality modulates sensorimotor cortical activity in healthy and hemiparetic subjects
- PMID: 23314780
- PMCID: PMC3762883
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2013.2238250
Visuomotor discordance during visually-guided hand movement in virtual reality modulates sensorimotor cortical activity in healthy and hemiparetic subjects
Abstract
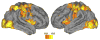
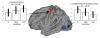
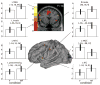
We investigated neural effects of visuomotor discordances during visually-guided finger movements. A functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)-compatible data glove was used to actuate (in real-time) virtual hand models shown on a display in first person perspective. In Experiment 1, we manipulated virtual hand motion to simulate either hypometric or unintentional (actuation of a mismatched finger) feedback of sequential finger flexion in healthy subjects. Analysis of finger motion revealed no significant differences in movement behavior across conditions, suggesting that between-condition differences in brain activity could only be attributed to varying modes of visual feedback rather than motor output. Hypometric feedback and mismatched finger feedback (relative to veridical) were associated with distinct activation. Hypometric feedback was associated with activation in the contralateral motor cortex. Mismatched feedback was associated with activation in bilateral ventral premotor, left dorsal premotor, and left occipitotemporal cortex. The time it took the subject to evaluate visuomotor discordance was positively correlated with activation in bilateral supplementary motor area, bilateral insula, right postcentral gyrus, bilateral dorsal premotor areas, and bilateral posterior parietal lobe. In Experiment 2, we investigated the effects of hypo- and hypermetric visual feedback in three stroke subjects. We observed increased activation of ipsilesional motor cortex in both hypometric and hypermetric feedback conditions. Our data indicate that manipulation of visual feedback of one's own hand movement may be used to facilitate activity in select brain networks. We suggest that these effects can be exploited in neurorehabilition to enhance the processes of brain reorganization after injury and, specifically, might be useful in aiding recovery of hand function in patients during virtual reality-based training.
Figures

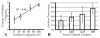
References
-
- Wise SP, et al. Changes in motor cortical activity during visuomotor adaptation. Exp Brain Res. 1998 Aug;121:285–99. - PubMed
-
- Patuzzo S, et al. Modulation of motor cortex excitability in the left hemisphere during action observation: a single- and paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation study of self- and non-self-action observation. Neuropsychologia. 2003;41:1272–8. - PubMed
-
- Mattar AA, Gribble PL. Motor learning by observing. Neuron. 2005 Apr 7;46:153–60. - PubMed
-
- Patton JL, et al. Evaluation of robotic training forces that either enhance or reduce error in chronic hemiparetic stroke survivors. Exp Brain Res. 2006 Jan;168:368–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

