Proteomic analysis of chromoplasts from six crop species reveals insights into chromoplast function and development
- PMID: 23314817
- PMCID: PMC3580812
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ers375
Proteomic analysis of chromoplasts from six crop species reveals insights into chromoplast function and development
Abstract
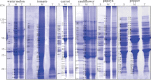
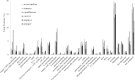
Chromoplasts are unique plastids that accumulate massive amounts of carotenoids. To gain a general and comparative characterization of chromoplast proteins, this study performed proteomic analysis of chromoplasts from six carotenoid-rich crops: watermelon, tomato, carrot, orange cauliflower, red papaya, and red bell pepper. Stromal and membrane proteins of chromoplasts were separated by 1D gel electrophoresis and analysed using nLC-MS/MS. A total of 953-2262 proteins from chromoplasts of different crop species were identified. Approximately 60% of the identified proteins were predicted to be plastid localized. Functional classification using MapMan bins revealed large numbers of proteins involved in protein metabolism, transport, amino acid metabolism, lipid metabolism, and redox in chromoplasts from all six species. Seventeen core carotenoid metabolic enzymes were identified. Phytoene synthase, phytoene desaturase, ζ-carotene desaturase, 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, and carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 1 were found in almost all crops, suggesting relative abundance of them among the carotenoid pathway enzymes. Chromoplasts from different crops contained abundant amounts of ATP synthase and adenine nucleotide translocator, which indicates an important role of ATP production and transport in chromoplast development. Distinctive abundant proteins were observed in chromoplast from different crops, including capsanthin/capsorubin synthase and fibrillins in pepper, superoxide dismutase in watermelon, carrot, and cauliflower, and glutathione-S-transferease in papaya. The comparative analysis of chromoplast proteins among six crop species offers new insights into the general metabolism and function of chromoplasts as well as the uniqueness of chromoplasts in specific crop species. This work provides reference datasets for future experimental study of chromoplast biogenesis, development, and regulation in plants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteome analysis of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) chromoplasts.Plant Cell Physiol. 2006 Dec;47(12):1663-73. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcl033. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17098784
-
Influence of chromoplast morphology on carotenoid bioaccessibility of carrot, mango, papaya, and tomato.Food Chem. 2012 Dec 15;135(4):2736-42. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.07.035. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22980866
-
Characterization under quasi-native conditions of the capsanthin/capsorubin synthase from Capsicum annuum L.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019 Oct;143:165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31505449
-
Chromoplast biogenesis and carotenoid accumulation.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013 Nov 15;539(2):102-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23851381 Review.
-
Biochemistry and molecular biology of carotenoid biosynthesis in chili peppers (Capsicum spp.).Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Sep 16;14(9):19025-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms140919025. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24065101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plastid transit peptides-where do they come from and where do they all belong? Multi-genome and pan-genomic assessment of chloroplast transit peptide evolution.PeerJ. 2020 Aug 27;8:e9772. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9772. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32913678 Free PMC article.
-
Plastid ribosomal protein S5 is involved in photosynthesis, plant development, and cold stress tolerance in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2016 Apr;67(9):2731-44. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw106. Epub 2016 Mar 22. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27006483 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory processes in non-photosynthetic plastids.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Jul 17;6:496. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00496. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26236317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of plastid-located phosphate transporters in carotenoid accumulation.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 15;13:1059536. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1059536. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36589064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of predicted plastid-targeted proteomes of sequenced higher plant genomes.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e112870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112870. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25393533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balsera M, Soll J, Buchanan BB. 2010. Redox extends its regulatory reach to chloroplast protein import. Trends in Plant Science 15, 515–521 - PubMed
-
- Barsan C, Sanchez-Bel P, Rombaldi C, Egea I, Rossignol M, Kuntz M, Zouine M, Latche A, Bouzayen M, Pech JC. 2010. Characteristics of the tomato chromoplast revealed by proteomic analysis. Journal of Experimental Botany 61, 2413–2431 - PubMed
-
- Baudisch B, Klosgen RB. 2012. Dual targeting of a processing peptidase into both endosymbiotic organelles mediated by a transport signal of unusual architecture. Molecular Plant 5, 494–503 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

