Toll-like receptor-8 agonistic activities in C2, C4, and C8 modified thiazolo[4,5-c]quinolines
- PMID: 23314908
- PMCID: PMC3577938
- DOI: 10.1039/c2ob26705e
Toll-like receptor-8 agonistic activities in C2, C4, and C8 modified thiazolo[4,5-c]quinolines
Abstract
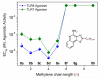
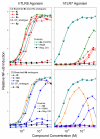
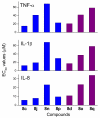
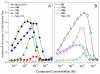
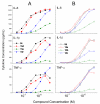
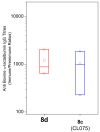
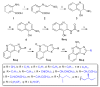
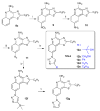
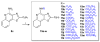
Toll-like receptor (TLR)-8 agonists typified by the 2-alkylthiazolo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine (CL075) chemotype are uniquely potent in activating adaptive immune responses by inducing robust production of T helper 1-polarizing cytokines, suggesting that TLR8-active compounds could be promising candidate vaccine adjuvants, especially for neonatal vaccines. Alkylthiazoloquinolines with methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl groups at C2 displayed comparable TLR8-agonistic potencies; activity diminished precipitously in the C2-pentyl compound, and higher homologues were inactive. The C2-butyl compound was unique in possessing substantial TLR7-agonistic activity. Analogues with branched alkyl groups at C2 displayed poor tolerance of terminal steric bulk. Virtually all modifications at C8 led to abrogation of agonistic activity. Alkylation on the C4-amine was not tolerated, whereas N-acyl analogues with short acyl groups (other than acetyl) retained TLR8 agonistic activity, but were substantially less water-soluble. Immunization in rabbits with a model subunit antigen adjuvanted with the lead C2-butyl thiazoloquinoline showed enhancements of antigen-specific antibody titers.
Figures
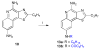
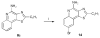
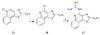

Similar articles
-
Structure-activity relationships in human toll-like receptor 7-active imidazoquinoline analogues.J Med Chem. 2010 Jun 10;53(11):4450-65. doi: 10.1021/jm100358c. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20481492 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based design of novel human Toll-like receptor 8 agonists.ChemMedChem. 2014 Apr;9(4):719-23. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201300573. Epub 2014 Jan 28. ChemMedChem. 2014. PMID: 24474703 Free PMC article.
-
Exquisite selectivity for human toll-like receptor 8 in substituted furo[2,3-c]quinolines.J Med Chem. 2013 Sep 12;56(17):6871-85. doi: 10.1021/jm400694d. Epub 2013 Aug 15. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23899291 Free PMC article.
-
Immunostimulatory activity of Toll-like receptor 8 agonists towards human leucocytes: basic mechanisms and translational opportunities.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1485-91. doi: 10.1042/BST0351485. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031250 Review.
-
[Structural Analyses of Toll-like Receptor Sensing Single-stranded Nucleic Acids and Its Application].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2016;136(2):173-8. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.15-00229-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 26831789 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Determinants of activity at human Toll-like receptors 7 and 8: quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) of diverse heterocyclic scaffolds.J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 9;57(19):7955-70. doi: 10.1021/jm500744f. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25192394 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging chemical patterns applied in predicting human toll-like receptor 8 agonists.Medchemcomm. 2018 Sep 21;9(11):1961-1971. doi: 10.1039/c8md00276b. eCollection 2018 Nov 1. Medchemcomm. 2018. PMID: 30568763 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like Receptor Agonist Conjugation: A Chemical Perspective.Bioconjug Chem. 2018 Mar 21;29(3):587-603. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00808. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Bioconjug Chem. 2018. PMID: 29378134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural evolution of toll-like receptor 7/8 agonists from imidazoquinolines to imidazoles.RSC Med Chem. 2021 May 14;12(7):1065-1120. doi: 10.1039/d1md00031d. eCollection 2021 Jul 21. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34355178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Adjuvantic Activity of Amphotericin B in a Novel, Multiplexed, Poly-TLR/NLR High-Throughput Screen.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 26;11(2):e0149848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149848. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26919709 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

