Intraamniotic lipopolysaccharide exposure changes cell populations and structure of the ovine fetal thymus
- PMID: 23314960
- PMCID: PMC3702021
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719112472742
Intraamniotic lipopolysaccharide exposure changes cell populations and structure of the ovine fetal thymus
Abstract
Rationale: Chorioamnionitis induces preterm delivery and acute involution of the fetal thymus which is associated with postnatal inflammatory disorders. We studied the immune response, cell composition, and architecture of the fetal thymus following intraamniotic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure.
Methods: Time-mated ewes received an intraamniotic injection of LPS 5, 12, or 24 hours or 2, 4, 8, or 15 days before delivery at 125 days gestational age (term = 150 days).
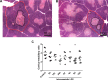
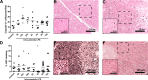
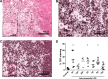
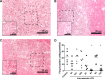
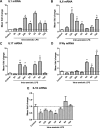
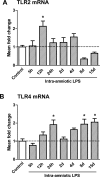
Results: The LPS exposure resulted in decreased blood lymphocytes within 5 hours and decreased thymic corticomedullary ratio within 24 hours. Thymic interleukin 6 (IL6) and IL17 messenger RNA (mRNA) increased 5-fold 24 hours post-LPS exposure. Increased toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) mRNA and nuclear factor κB positive cells at 24 hours after LPS delivery demonstrated acute thymic activation. Both TLR4 and IL1 mRNA increased by 5-fold and the number of Foxp3-positive cells (Foxp3+ cells) decreased 15 days after exposure.
Conclusion: Intraamniotic LPS exposure caused a proinflammatory response, involution, and a persistent depletion of thymic Foxp3+ cells indicating disturbance of the fetal immune homeostasis.
Keywords: fetal inflammatory response syndrome; immune modulation; prematurity; thymic involution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(20):1500–1507. - PubMed
-
- Redline RW. Placental inflammation. Semin Neonatol. 2004;9(4):265–274. - PubMed
-
- Hagberg H, Wennerholm UB, Savman K. Sequelae of chorioamnionitis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2002;15(3):301–306. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(20):1500–1507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

