A genomewide mutagenesis screen identifies multiple genes contributing to Vi capsular expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi
- PMID: 23316043
- PMCID: PMC3592008
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01632-12
A genomewide mutagenesis screen identifies multiple genes contributing to Vi capsular expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi
Abstract
A transposon-based, genomewide mutagenesis screen exploiting the killing activity of a lytic ViII bacteriophage was used to identify Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi genes that contribute to Vi polysaccharide capsule expression. Genes enriched in the screen included those within the viaB locus (tviABCDE and vexABCDE) as well as oxyR, barA/sirA, and yrfF, which have not previously been associated with Vi expression. The role of these genes in Vi expression was confirmed by constructing defined null mutant derivatives of S. Typhi, and these were negative for Vi expression as determined by agglutination assays with Vi-specific sera or susceptibility to Vi-targeting bacteriophages. Transcriptome analysis confirmed a reduction in expression from the viaB locus in these S. Typhi mutant derivatives and defined regulatory networks associated with Vi expression.
Figures
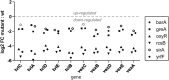
Similar articles
-
OxyR positively and directly regulates Vi polysaccharide capsular antigen in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.Microb Pathog. 2018 Nov;124:191-197. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.08.050. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30145252
-
Vi Capsular Polysaccharide Produced by Recombinant Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi A Confers Immunoprotection against Infection by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Apr 24;7:135. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00135. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28484685 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the viaB locus encoding the biosynthetic machinery for Vi capsule formation in Salmonella Typhi.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045609. Epub 2012 Sep 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029132 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Vi Negative Isolates of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhi.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1052:9-18. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7572-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29785477 Review.
-
The genome of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jul 15;45 Suppl 1:S29-33. doi: 10.1086/518143. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17582565 Review.
Cited by
-
DEG 10, an update of the database of essential genes that includes both protein-coding genes and noncoding genomic elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(Database issue):D574-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1131. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24243843 Free PMC article.
-
A decade of advances in transposon-insertion sequencing.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 Sep;21(9):526-540. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0244-x. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32533119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Approaches to querying bacterial genomes with transposon-insertion sequencing.RNA Biol. 2013 Jul;10(7):1161-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.24765. Epub 2013 Apr 23. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23635712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial strategies for improving multiple-stress resistance in industrially relevant Escherichia coli strains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Oct;80(19):6223-42. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01542-14. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25085490 Free PMC article.
-
Collateral sensitivity increases the efficacy of a rationally designed bacteriophage combination to control Salmonella enterica.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0147623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01476-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38376991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sonnenburg JL, Xu J, Leip DD, Chen CH, Westover BP, Weatherford J, Buhler JD, Gordon JI. 2005. Glycan foraging in vivo by an intestine-adapted bacterial symbiont. Science 307:1955–1959 - PubMed
-
- Labrie SJ, Samson JE, Moineau S. 2010. Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nat. Rev. 8:317–327 - PubMed
-
- Leid JG, Willson CJ, Shirtliff ME, Hassett DJ, Parsek MR, Jeffers AK. 2005. The exopolysaccharide alginate protects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria from IFN-gamma-mediated macrophage killing. J. Immunol. 175:7512–7518 - PubMed
-
- Pickard D, Toribio AL, Petty NK, van Tonder A, Yu L, Goulding D, Barrell B, Rance R, Harris D, Wetter M, Wain J, Choudhary J, Thomson N, Dougan G. 2010. A conserved acetyl esterase domain targets diverse bacteriophages to the Vi capsular receptor of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. J. Bacteriol. 192:5746–5754 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

