Structure and dynamic regulation of Abl kinases
- PMID: 23316053
- PMCID: PMC3581414
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R112.438382
Structure and dynamic regulation of Abl kinases
Abstract
The c-abl proto-oncogene encodes a unique protein-tyrosine kinase (Abl) distinct from c-Src, c-Fes, and other cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. In normal cells, Abl plays prominent roles in cellular responses to genotoxic stress as well as in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Abl is also well known in the context of Bcr-Abl, the oncogenic fusion protein characteristic of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Selective inhibitors of Bcr-Abl, of which imatinib is the prototype, have had a tremendous impact on clinical outcomes in chronic myelogenous leukemia and revolutionized the field of targeted cancer therapy. In this minireview, we focus on the structural organization and dynamics of Abl kinases and how these features influence inhibitor sensitivity.
Figures

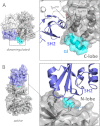
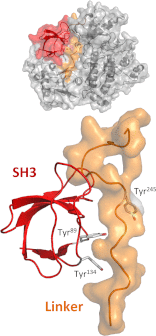
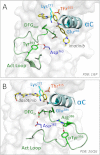
References
-
- Hantschel O., Superti-Furga G. (2004) Regulation of the c-Abl and Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 33–44 - PubMed
-
- Pendergast A. M. (2002) The Abl family kinases: mechanisms of regulation and signaling. Adv. Cancer Res. 85, 51–100 - PubMed
-
- Van Etten R. A. (1999) Cycling, stressed-out and nervous: cellular functions of c-Abl. Trends Cell Biol. 9, 179–186 - PubMed
-
- Pluk H., Dorey K., Superti-Furga G. (2002) Autoinhibition of c-Abl. Cell 108, 247–259 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

