Oxidative activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-activated kinase II mediates ER stress-induced cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis
- PMID: 23316062
- PMCID: PMC3602775
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00752.2012
Oxidative activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-activated kinase II mediates ER stress-induced cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis
Abstract
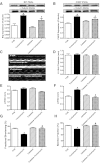
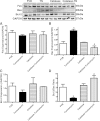
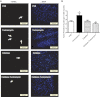
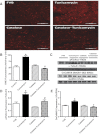
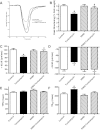
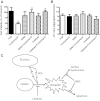
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress elicits oxidative stress and intracellular Ca(2+) derangement via activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). This study was designed to examine the role of CaMKII in ER stress-induced cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis as well as the effect of antioxidant catalase. Wild-type FVB and transgenic mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of catalase were challenged with the ER stress inducer tunicamycin (3 mg/kg ip for 48 h). Presence of ER stress was verified using the ER stress protein markers immunoglobulin binding protein (BiP) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), the effect of which was unaffected by catalase overexpression. Echocardiographic assessment revealed that tunicamycin elicited cardiac remodeling (enlarged end-systolic diameter without affecting diastolic and ventricular wall thickness), depressed fractional shortening, ejection fraction, and cardiomyocyte contractile capacity, intracellular Ca(2+) mishandling, accumulation of reactive oxygen species (superoxide production and NADPH oxidase p47phox level), CaMKII oxidation, and apoptosis (evidenced by Bax, Bcl-2/Bax ratio, and TUNEL staining), the effects of which were obliterated by catalase. Interestingly, tunicamycin-induced cardiomyocyte mechanical anomalies and cell death were ablated by the CaMKII inhibitor KN93, in a manner reminiscent of catalase. These data favored a permissive role of oxidative stress and CaMKII activation in ER stress-induced cardiac dysfunction and cell death. Our data further revealed the therapeutic potential of antioxidant or CaMKII inhibition in cardiac pathological conditions associated with ER stress. This research shows for the first time that contractile dysfunction caused by ER stress is a result of the oxidative activation of the CaMKII pathway.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

