Systems biology of cancer: moving toward the integrative study of the metabolic alterations in cancer cells
- PMID: 23316163
- PMCID: PMC3539652
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00481
Systems biology of cancer: moving toward the integrative study of the metabolic alterations in cancer cells
Abstract
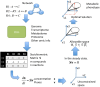
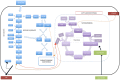
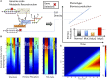
One of the main objectives in systems biology is to understand the biological mechanisms that give rise to the phenotype of a microorganism by using high-throughput technologies (HTs) and genome-scale mathematical modeling. The computational modeling of genome-scale metabolic reconstructions is one systemic and quantitative strategy for characterizing the metabolic phenotype associated with human diseases and potentially for designing drugs with optimal clinical effects. The purpose of this short review is to describe how computational modeling, including the specific case of constraint-based modeling, can be used to explore, characterize, and predict the metabolic capacities that distinguish the metabolic phenotype of cancer cell lines. As we show herein, this computational framework is far from a pure theoretical description, and to ensure proper biological interpretation, it is necessary to integrate high-throughput data and generate predictions for later experimental assessment. Hence, genome-scale modeling serves as a platform for the following: (1) the integration of data from HTs, (2) the assessment of how metabolic activity is related to phenotype in cancer cell lines, and (3) the design of new experiments to evaluate the outcomes of the in silico analysis. By combining the functions described above, we show that computational modeling is a useful methodology to construct an integrative, systemic, and quantitative scheme for understanding the metabolic profiles of cancer cell lines, a first step to determine the metabolic mechanism by which cancer cells maintain and support their malignant phenotype in human tissues.
Keywords: cancer metabolic phenotype; computational modeling of metabolism; constraint-based modeling; genome scale metabolic reconstruction; high throughput biology.
Figures
References
-
- Bishop J. M., Weinberg R. A. (ed.). (1996). Molecular Oncology. New York, NY: Scientific American, Inc
-
- Braun R. D., Lanzen J. L., Snyder S. A., Dewhirst M. W. (2001). Comparison of tumor and normal tissue oxygen tension measurements using OxyLite or microelectrodes in rodents. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 280, H2533–H2544 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

