Cholesterol homeostasis: a key to prevent or slow down neurodegeneration
- PMID: 23316166
- PMCID: PMC3539713
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00486
Cholesterol homeostasis: a key to prevent or slow down neurodegeneration
Abstract
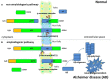
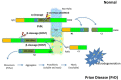
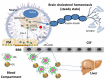
Neurodegeneration, a common feature for many brain disorders, has severe consequences on the mental and physical health of an individual. Typically human neurodegenerative diseases are devastating illnesses that predominantly affect elderly people, progress slowly, and lead to disability and premature death; however they may occur at all ages. Despite extensive research and investments, current therapeutic interventions against these disorders treat solely the symptoms. Therefore, since the underlying mechanisms of damage to neurons are similar, in spite of etiology and background heterogeneous, it will be of interest to identify possible trigger point of neurodegeneration enabling development of drugs and/or prevention strategies that target many disorders simultaneously. Among the factors that have been identified so far to cause neurodegeneration, failures in cholesterol homeostasis are indubitably the best investigated. The aim of this review is to critically discuss some of the main results reported in the recent years in this field mainly focusing on the mechanisms that, by recovering perturbations of cholesterol homeostasis in neuronal cells, may correct clinically relevant features occurring in different neurodegenerative disorders and, in this regard, also debate the current potential therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: cholesterol esterification; cholesterol homeostasis; drug targets; neurodegenerative disorders; neuronal membranes.
Figures

References
-
- Anchisi L., Dessì S., Pani A., Mandas A. (2013). Neutral lipid determination in peripheral blood mononuclear cells: a useful tool for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in dementia. J. Mol. Biomar. Diag. 3:1000136 http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2155-9929.1000136 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

