AKTivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by KSHV
- PMID: 23316192
- PMCID: PMC3539662
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00401
AKTivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by KSHV
Abstract
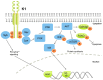
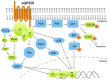
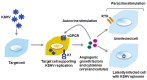
As an obligate intracellular parasite, Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) relies on the host cell machinery to meet its needs for survival, viral replication, production, and dissemination of progeny virions. KSHV is a gammaherpesvirus that is associated with three different malignancies: Kaposi sarcoma (KS), and two B cell lymphoproliferative disorders, primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) and multicentric Castleman's disease. KSHV viral proteins modulate the cellular phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, which is a ubiquitous pathway that also controls B lymphocyte proliferation and development. We review the mechanisms by which KSHV manipulates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, with a specific focus on B cells.
Keywords: Akt; B cells; KSHV; PI3K; mTOR.
Figures
References
-
- Ambinder R. F., Cesarman E. (2007). “Clinical and pathological aspects of EBV and KSHV infection,” in Human Herpesviruses Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis, edsArvin A., Campadelli-Fiume G., Moore P. S. (New York: Cambridge University Press; ) 885–914 - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y., Tosato G. (1999). Role of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in the pathogenesis of Kaposi’s sarcoma- associated herpesvirus- infected primary effusion lymphomas. Blood 94 4247–4254 - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y., Yarchoan R., Braun J., Iwamoto A., Tosato G. (2000). Viral and cellular cytokines in AIDS-related malignant lymphomatous effusions. Blood 96 1599–1601 - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y., Yarchoan R., Wyvill K., Okamoto S., Little R. F., Tosato G. (2001). Detection of viral interleukin-6 in Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-linked disorders. Blood 97 2173–2176 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

