ATP release and purinergic signaling in NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 23316199
- PMCID: PMC3539150
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00414
ATP release and purinergic signaling in NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
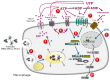
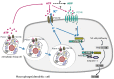
The NLRP3 inflammasome is a protein complex involved in IL-1β and IL-18 processing that senses pathogen- and danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs and DAMPs). One step- or two step-models have been proposed to explain the tight regulation of IL-1β production during inflammation. Moreover, cellular stimulation triggers adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release and subsequent activation of purinergic receptors at the cell surface. Importantly some studies have reported roles for extracellular ATP, in NLRP3 inflammasome activation in response to PAMPs and DAMPs. In this mini review, we will discuss the link between active ATP release, purinergic signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. We will focus on the role of autocrine or paracrine ATP export in particle-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and discuss how particle activators are competent to induce maturation and secretion of IL-1β through a process that involves, as a first event, extracellular release of endogenous ATP through hemichannel opening, and as a second event, signaling through purinergic receptors that trigger NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Finally, we will review the evidence for ATP as a key pro-inflammatory mediator released by dying cells. In particular we will discuss how cancer cells dying via autophagy trigger ATP-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the macrophages engulfing them, eliciting an immunogenic response against tumors.
Keywords: ATP; NLRP3; P2R; autophagic cell death; danger signal; inflammasome; purinergic signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Boeynaems J. M., Barnard E. A., Boyer J. L., Kennedy C., et al. (2006). International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 58 281–341 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aganna E., Martinon F., Hawkins P. N., Ross J. B., Swan D. C., Booth D. R., et al. (2002). Association of mutations in the NALP3/CIAS1/PYPAF1 gene with a broad phenotype including recurrent fever, cold sensitivity, sensorineural deafness, and AA amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 46 2445–2452 - PubMed
-
- Agostini L., Martinon F., Burns K., Mcdermott M. F., Hawkins P. N., Tschopp J. (2004). NALP3 forms an IL-1beta-processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle–Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity 20 319–325 - PubMed
-
- Ataman-Onal Y., Munier S., Ganee A., Terrat C., Durand P. Y., Battail N., et al. (2006). Surfactant-free anionic PLA nanoparticles coated with HIV-1 p24 protein induced enhanced cellular and humoral immune responses in various animal models. J. Control. Release 112 175–185 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

