Leptin locally synthesized in carotid atherosclerotic plaques could be associated with lesion instability and cerebral emboli
- PMID: 23316287
- PMCID: PMC3541612
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.112.001727
Leptin locally synthesized in carotid atherosclerotic plaques could be associated with lesion instability and cerebral emboli
Abstract
Background: Unstable carotid plaques cause cerebral emboli. Leptin promotes atherosclerosis and vessel wall remodeling. We hypothesized that carotid atherosclerotic lesion instability is associated with local leptin synthesis.
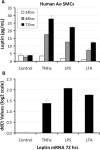
Methods and results: Carotid endarterectomy plaques from symptomatic (n=40) and asymptomatic patients with progressive stenosis (n=38) were analyzed for local expression of leptin, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. All lesions exhibited advanced atherosclerosis inclusive of thick- and thin-cap fibroatheromas or lesion rupture. Symptomatic lesions exhibited more plaque ruptures and macrophage infiltration (P=0.001 and P=0.05, respectively). Symptomatic plaques showed preferential leptin, TNF-α, and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 transcript (P=0.03, P=0.04, and P=0.05, respectively). Leptin mRNA and antigen in macrophages and smooth muscle cells were confirmed by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Plasma leptin levels were not significantly different between groups (P=1.0), whereas TNF-α was significantly increased in symptomatic patients (P=0.006). Human aortic smooth muscle cell culture stimulated by TNF-α, lipopolysaccharide, or lipoteichoic acid revealed 6-, 6.7-, and 6-fold increased secreted leptin antigen, respectively, at 72 hours (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Neurologically symptomatic patients overexpress leptin mRNA and synthesize leptin protein in carotid plaque macrophages and smooth muscle cells. Local leptin induction, presumably by TNF-α, could exert paracrine or autocrine effects, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of lesion instability.
Clinical trial registration: URL: www.Clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00449306.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; leptin; macrophages; smooth muscle cells; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Leptin receptor is elevated in carotid plaques from neurologically symptomatic patients and positively correlated with augmented macrophage density.J Vasc Surg. 2008 Nov;48(5):1146-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2008.06.054. Epub 2008 Sep 30. J Vasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 18829234
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α regulates p27 kip expression and apoptosis in smooth muscle cells of human carotid plaques via forkhead transcription factor O1.Exp Mol Pathol. 2011 Feb;90(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Exp Mol Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21075101 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinolysis inhibitors in plaque stability: a morphological association of PAI-1 and TAFI in advanced carotid plaque.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Apr;15(4):758-769. doi: 10.1111/jth.13641. Epub 2017 Feb 28. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28135035
-
Inflammation in human carotid atheroma plaques.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018 Feb;39:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.01.006. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018. PMID: 29396056 Review.
-
A review of carotid atherosclerosis and vascular cognitive decline: a new understanding of the keys to symptomology.Neurosurgery. 2010 Aug;67(2):484-93; discussion 493-4. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000371730.11404.36. Neurosurgery. 2010. PMID: 20644437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Local Application of Leptin Antagonist Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Ascending Aortic Aneurysm and Cardiac Remodeling.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 May 3;5(5):e003474. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003474. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27143353 Free PMC article.
-
Local perivascular adiponectin associates with lower extremity vascular operative wound complications.Surgery. 2016 Jul;160(1):204-210. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.01.024. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Surgery. 2016. PMID: 27085683 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Interplay of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Inflammation in Transition Dairy Cows.Animals (Basel). 2024 Mar 8;14(6):832. doi: 10.3390/ani14060832. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin resistance increases as days on feed advance in feedlot Bos indicus beef cattle offered a high-concentrate finishing diet.J Anim Sci. 2022 Jul 1;100(7):skac182. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac182. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35580854 Free PMC article.
-
A proposed model to evaluate how changes in body condition score and the fatty acid profile of a supplement affect physiology and metabolic responses of nonlactating females.JDS Commun. 2023 Jul 13;4(5):406-411. doi: 10.3168/jdsc.2022-0349. eCollection 2023 Sep. JDS Commun. 2023. PMID: 37727238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beltowski J. Leptin and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2006;189:47-60. - PubMed
-
- Loftus IM, Naylor AR, Goodall S, Crowther M, Jones L, Bell PR, Thompson MM. Increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in unstable carotid plaques: a potential role in acute plaque disruption. Stroke. 2000;31:40-47. - PubMed
-
- Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP, Narula J. Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2054-2061. - PubMed
-
- Fantuzzi G, Faggioni R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;68:437-446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

