Resting heart rate and the risk of microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 23316296
- PMCID: PMC3541618
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.112.002832
Resting heart rate and the risk of microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: A higher resting heart rate is associated with an increased probability of cardiovascular complications and premature death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The impact of heart rate on the risk of developing microvascular complications, such as diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy, is, however, unknown. The present study tests the hypothesis that a higher resting heart rate is associated with an increased incidence and a greater progression of microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
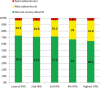
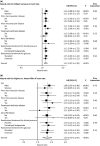
Methods and results: The relation between baseline resting heart rate and the development of a major microvascular event was examined in 11 140 patients who participated in the Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) study. Major microvascular events were defined as a composite of new or worsening nephropathy or new or worsening retinopathy. Patients with a higher baseline heart rate were at increased risk of a new major microvascular complication during follow-up (adjusted hazard ratio: 1.13 per 10 beats per minute; 95% confidence interval: 1.07-1.20; P<0.001). The excess hazard was evident for both nephropathy (adjusted hazard ratio: 1.16 per 10 beats per minute; 95% confidence interval: 1.08-1.25) and retinopathy (adjusted hazard ratio: 1.11 per 10 beats per minute; 95% confidence interval: 1.02-1.21).
Conclusion: Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have a higher resting heart rate experience a greater incidence of new-onset or progressive nephropathy and retinopathy.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00145925. http://www.advance-trial.com/static/html/prehome/prehome.asp.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, type 2; heart rate; microcirculation.
Figures
References
-
- The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial research group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977-986. - PubMed
-
- Rajala U, Pajunpaa H, Koskela P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S. High cardiovascular disease mortality in subjects with visual impairment caused by diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:957-961. - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Cruickshanks KJ. Association of ocular disease and mortality in a diabetic population. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999;117:1487-1495. - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, Halle JP, Young J, Rashkow A, Joyce C, Nawaz S, Yusuf S. Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA. 2001;286:421-426. - PubMed

