Haemorrhagic colitis caused by dasatinib
- PMID: 23316400
- PMCID: PMC3539334
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/417106
Haemorrhagic colitis caused by dasatinib
Abstract
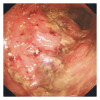
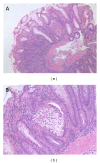
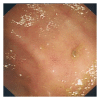
Gastrointestinal bleeding appears to be a common adverse event associated with dasatinib therapy. Here we present a case of a 59-year-old man with chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) developing the rarest complication of haemorrhagic colitis with dasatinib therapy which resolved rapidly after treatment withdrawal.
Figures
References
-
- Talpaz M, Shah NP, Kantarjian H, et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354(24):2531–2541. - PubMed
-
- Lombardo LJ, Lee FY, Chen P, et al. Discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)- piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino)thiazole-5-carboxamide (BMS-354825), a dual Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical assays. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2004;47(27):6658–6661. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

