Common variants of Drosophila melanogaster Cyp6d2 cause camptothecin sensitivity and synergize with loss of Brca2
- PMID: 23316441
- PMCID: PMC3538347
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.112.003996
Common variants of Drosophila melanogaster Cyp6d2 cause camptothecin sensitivity and synergize with loss of Brca2
Abstract
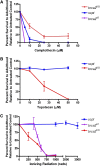
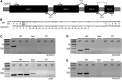
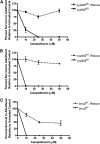
Many chemotherapeutic agents selectively target rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells, by causing DNA damage that leads to genome instability and cell death. We used Drosophila melanogaster to study how mutations in key DNA repair genes affect an organism's response to chemotherapeutic drugs. In this study, we focused on camptothecin and its derivatives, topotecan and irinotecan, which are type I topoisomerase inhibitors that create DNA double-strand breaks in rapidly dividing cells. Here, we describe two polymorphisms in Drosophila Cyp6d2 that result in extreme sensitivity to camptothecin but not topotecan or irinotecan. We confirmed that the sensitivity was due to mutations in Cyp6d2 by rescuing the defect with a wild-type copy of Cyp6d2. In addition, we showed that combining a cyp6d2 mutation with mutations in Drosophila brca2 results in extreme sensitivity to camptothecin. Given the frequency of the Cyp6d2 polymorphisms in publcly available Drosophila stocks, our study demonstrates the need for caution when interpreting results from drug sensitivity screens in Drosophila and other model organisms. Furthermore, our findings illustrate how genetic background effects can be important when determining the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents in various DNA repair mutants.
Keywords: chemotherapeutics; cytochrome p450; double-strand breaks; homologous recombination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Topoisomerase degradation, DSB repair, p53 and IAPs in cancer cell resistance to camptothecin-like topoisomerase I inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1835(1):11-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23006513 Review.
-
Genome-wide mRNA and microRNA profiling of the NCI 60 cell-line screen and comparison of FdUMP[10] with fluorouracil, floxuridine, and topoisomerase 1 poisons.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Dec;9(12):3105-14. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0674. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 21159603 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of camptothecin derivatives presently in clinical trials: genotoxic potency and mitotic recombination.Mutagenesis. 2002 Mar;17(2):141-7. doi: 10.1093/mutage/17.2.141. Mutagenesis. 2002. PMID: 11880543
-
Protein expression of DNA damage repair proteins dictates response to topoisomerase and PARP inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0119614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119614. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25774912 Free PMC article.
-
The role of single strand break repair pathways in cellular responses to camptothecin induced DNA damage.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 May;125:109875. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109875. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32036211 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA polymerase theta suppresses mitotic crossing over.PLoS Genet. 2021 Mar 22;17(3):e1009267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009267. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33750946 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Repair in Drosophila: Mutagens, Models, and Missing Genes.Genetics. 2017 Feb;205(2):471-490. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.186759. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28154196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homology directed repair is unaffected by the absence of siRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 30;44(17):8261-71. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw570. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27353331 Free PMC article.
-
Annealing of Complementary DNA Sequences During Double-Strand Break Repair in Drosophila Is Mediated by the Ortholog of SMARCAL1.Genetics. 2017 May;206(1):467-480. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.200238. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28258182 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila melanogaster PIF1 Helicase Promotes Survival During Replication Stress and Processive DNA Synthesis During Double-Strand Gap Repair.Genetics. 2019 Nov;213(3):835-847. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302665. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31537623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams M. D., Celniker S. E., Holt R. A., Evans C. A., Gocayne J. D., et al. , 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185–2195 - PubMed
-
- Amichot M., Tarès S., Brun-Barale A., Arthaud L., Bride J.-M., et al. , 2004. Point mutations associated with insecticide resistance in the Drosophila cytochrome P450 Cyp6a2 enable DDT metabolism. Eur. J. Biochem. 271: 1250–1257 - PubMed
-
- Boulton S. J., 2006. Cellular functions of the BRCA tumour-suppressor proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34: 633–645 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
