Age of red blood cells and transfusion in critically ill patients
- PMID: 23316800
- PMCID: PMC3575378
- DOI: 10.1186/2110-5820-3-2
Age of red blood cells and transfusion in critically ill patients
Abstract
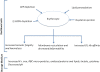
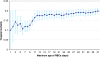
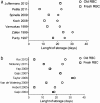
Red blood cells (RBC) storage facilitates the supply of RBC to meet the clinical demand for transfusion and to avoid wastage. However, RBC storage is associated with adverse changes in erythrocytes and their preservation medium. These changes are responsible for functional alterations and for the accumulation of potentially injurious bioreactive substances. They also may have clinically harmful effects especially in critically ill patients. The clinical consequences of storage lesions, however, remain a matter of persistent controversy. Multiple retrospective, observational, and single-center studies have reported heterogeneous and conflicting findings about the effect of blood storage duration on morbidity and/or mortality in trauma, cardiac surgery, and intensive care unit patients. Describing the details of this controversy, this review not only summarizes the current literature but also highlights the equipoise that currently exists with regard to the use of short versus current standard (extended) storage duration red cells in critically ill patients and supports the need for large, randomized, controlled trials evaluating the clinical impact of transfusing fresh (short duration of storage) versus older (extended duration of storage) red cells in critically ill patients.
Figures
References
-
- Corwin HL, Gettinger A, Pearl RG, Fink MP, Levy MM, Abraham E, MacIntyre NR, Shabot MM, Duh MS, Shapiro MJ. The CRIT Study: Anemia and blood transfusion in the critically ill–current clinical practice in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:39–52. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000104112.34142.79. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Westbrook A, Pettilä V, Nichol A, Bailey MJ, Syres G, Murray L, Bellomo R, Wood E, Phillips LE, Street A, French C, Orford N, Santamaria J, Cooper DJ. Blood Observational Study Investigators of ANZICS-Clinical Trials Group. Transfusion practice and guidelines in Australian and New Zealand intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:1138–1146. - PubMed
-
- Musallam KM, Tamim HM, Richards T, Spahn DR, Rosendaal FR, Habbal A, Khreiss M, Dahdaleh FS, Khavandi K, Sfeir PM. et al.Preoperative anaemia and postoperative outcomes in non-cardiac surgery: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2011;378:1396–1407. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61381-0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

