Phospho switch triggers Brd4 chromatin binding and activator recruitment for gene-specific targeting
- PMID: 23317504
- PMCID: PMC3595396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.006
Phospho switch triggers Brd4 chromatin binding and activator recruitment for gene-specific targeting
Abstract
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (Brd4) is an epigenetic reader and transcriptional regulator recently identified as a cancer therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukemia, multiple myeloma, and Burkitt's lymphoma. Although chromatin targeting is a crucial function of Brd4, there is little understanding of how bromodomains that bind acetylated histones are regulated, nor how the gene-specific activity of Brd4 is determined. Via interaction screen and domain mapping, we identified p53 as a functional partner of Brd4. Interestingly, Brd4 association with p53 is modulated by casein kinase II (CK2)-mediated phosphorylation of a conserved acidic region in Brd4 that selectively contacts either a juxtaposed bromodomain or an adjacent basic region to dictate the ability of Brd4 binding to chromatin and also the recruitment of p53 to regulated promoters. The unmasking of bromodomains and activator recruitment, concurrently triggered by the CK2 phospho switch, provide an intriguing mechanism for gene-specific targeting by a universal epigenetic reader.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
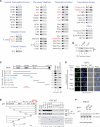
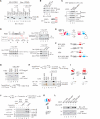



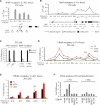

Comment in
-
Anything but simple: a phosphorylation-driven toggle within Brd4 triggers gene-specific transcriptional activation.Mol Cell. 2013 Mar 7;49(5):838-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.02.021. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23473602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsarraj J, Walker RC, Webster JD, Geiger TR, Crawford NP, Simpson RM, Ozato K, Hunter KW. Deletion of the proline-rich region of the murine metastasis susceptibility gene Brd4 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition- and stem cell-like conversion. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3121–3131. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Claudio PP, Cui J, Ghafouri M, Mariano C, White MK, Safak M, Sheffield JB, Giordano A, Khalili K, Amini S, Sawaya BE. Cdk9 phosphorylates p53 on serine 392 independently of CKII. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006;208:602–612. - PubMed
-
- Dawson MA, Prinjha RK, Dittman A, Giotopoulos G, Bantscheff M, Chan WI, Robson SC, Chung CW, Hopf C, Savitski MM, Huthmacher C, Gudgin E, Lugo D, Beinke S, Chapman TD, Roberts EJ, Soden PE, Auger KR, Mirguet O, Doehner K, Delwel R, Burnett AK, Jeffrey P, Drewes G, Lee K, Huntly BJ, Kouzarides T. Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia. Nature. 2011;478:529–533. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB, Shi J, Jacobs HM, Kastritis E, Gilpatrick T, Paranal RM, Qi J, Chesi M, Schinzel AC, McKeown MR, Heffernan TP, Vakoc CR, Bergsagel PL, Ghobrial IM, Richardson PG, Young RA, Hahn WC, Anderson KC, Kung AL, Bradner JE, Mitsiades CS. BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell. 2011;146:904–917. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

