Chronic angiotensin-II treatment potentiates HR slowing in Sprague-Dawley rat during acute behavioral stress
- PMID: 23317537
- PMCID: PMC3595344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.12.004
Chronic angiotensin-II treatment potentiates HR slowing in Sprague-Dawley rat during acute behavioral stress
Abstract
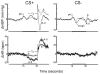
This study examined the effect of 2-week infusion of angiotensin-II (Ang-II; 175 ng/kg/min) via minipump in rats (n=7) upon the mean arterial blood pressure (mBP) and heart rate (HR) response to an acute stress as compared to rats infused with saline (n=7). The acute stress was produced by a classical aversive conditioning paradigm: a 15s tone (CS+) followed by a half second tail shock. Baseline mBP in Ang-II infused rats (167.7±21.3 mm Hg; mean±SD) significantly exceeded that of controls (127.6±13.5 mm Hg). Conversely, baseline HR in the Ang-II infused rats (348±33) was significantly lower than controls (384±19 bpm). The magnitude of the mBP increase during CS+ did not differ between groups, but the HR slowing during CS+ in the Ang-II infused rats (-13.2±8.9 bpm) was significantly greater than that seen in controls (-4.2±5.5 bpm). This augmented bradycardia may be inferentially attributed to an accentuated increase in cardiac parasympathetic activity during CS+ in the Ang-II infused rats. The mBP increased above baseline immediately post-shock delivery in controls, but fell in the Ang-II infused rats, perhaps because of a 'ceiling effect' in total vascular resistance. This classical conditioning model of 'acute stress' differs from most stress paradigms in rats in yielding a HR slowing concomitant with a pressor response, and this slowing is potentiated by Ang-II.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- American Physiological Society Guiding principles for research involving animals and human beings. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2002;283:R281–R283. - PubMed
-
- Binkley PF, Haas GJ, Starling RC, Nunziata E, Hatton PA, Leier CF, Cody RJ. Sustained augmentation of parasympathetic tone with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;21:655–661. - PubMed
-
- Brown DR, Li S-G, Lawler JE, Randall DC. Sympathetic control of BP and BP variability in borderline hypertensive rats on high- vs. low-salt diet. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1999;277:R650–R657. - PubMed
-
- Burgess DE, Hundley JC, Li S, Randall DC, Brown DR. Multifiber renal sympathetic nerve activity recordings predict mean arterial blood pressure in unanesthetized rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1997;273:R851–R857. - PubMed
-
- Cassis LA, Marshall DE, Fettinger MJ, Rosenbluth B, Lodder RA. Mechanisms contributing to angiotensin II regulation of body weight. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 1998;274:E867–E876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

