Regulation of blood-testis barrier (BTB) dynamics during spermatogenesis via the "Yin" and "Yang" effects of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2
- PMID: 23317821
- PMCID: PMC4086807
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407704-1.00006-3
Regulation of blood-testis barrier (BTB) dynamics during spermatogenesis via the "Yin" and "Yang" effects of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2
Abstract
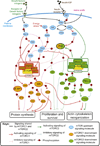
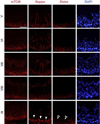
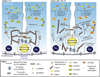
In mammalian testes, haploid spermatozoa are formed from diploid spermatogonia during spermatogenesis, which is a complicated cellular process. While these cellular events were reported in the 1960s and 1970s, the underlying molecular mechanism(s) that regulates these events remained unexplored until the past ∼10 years. For instance, adhesion proteins were shown to be integrated components at the Sertoli cell-cell interface and/or the Sertoli-spermatid interface in the late 1980s. But only until recently, studies have demonstrated that some of the adhesion proteins serve as the platform for signal transduction that regulates cell adhesion. In this chapter, a brief summary and critical discussion are provided on the latest findings regarding these cell-adhesion proteins in the testis and their relationship to spermatogenesis. Moreover, antagonistic effects of two mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complexes, known as mTORC1 and mTORC2, on cell-adhesion function in the testis are discussed. Finally, a hypothetic model is presented to depict how these two mTOR-signaling complexes having the "yin" and "yang" antagonistic effects on the Sertoli cell tight junction (TJ)-permeability barrier can maintain the blood-testis barrier (BTB) integrity during the epithelial cycle while preleptotene spermatocytes are crossing the BTB.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTOR) pathway modulates blood-testis barrier (BTB) function through F-actin organization and gap junction.Histol Histopathol. 2016 Sep;31(9):961-8. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-753. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Histol Histopathol. 2016. PMID: 26957088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basement Membrane Laminin α2 Regulation of BTB Dynamics via Its Effects on F-Actin and Microtubule Cytoskeletons Is Mediated Through mTORC1 Signaling.Endocrinology. 2017 Apr 1;158(4):963-978. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1630. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28323988 Free PMC article.
-
Rictor/mTORC2 regulates blood-testis barrier dynamics via its effects on gap junction communications and actin filament network.FASEB J. 2013 Mar;27(3):1137-52. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-212977. Epub 2013 Jan 3. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23288930 Free PMC article.
-
rpS6 regulates blood-testis barrier dynamics through Arp3-mediated actin microfilament organization in rat sertoli cells. An in vitro study.Endocrinology. 2015 May;156(5):1900-13. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1791. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25714812 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and spermatogenesis.Hum Reprod Update. 2013 Mar-Apr;19(2):167-86. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dms049. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Hum Reprod Update. 2013. PMID: 23287428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Focal adhesion kinase and actin regulatory/binding proteins that modulate F-actin organization at the tissue barrier: Lesson from the testis.Tissue Barriers. 2013 Apr 1;1(2):e24252. doi: 10.4161/tisb.24252. Tissue Barriers. 2013. PMID: 24665388 Free PMC article.
-
Olaquindox disrupts tight junction integrity and cytoskeleton architecture in mouse Sertoli cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 16;8(51):88630-88644. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20289. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179463 Free PMC article.
-
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection Compromises the Blood-Testis Barrier by Disturbing mTORC1-mTORC2 Balance.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 19;12:582858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.582858. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679734 Free PMC article.
-
The cell-cell junctions of mammalian testes: I. The adhering junctions of the seminiferous epithelium represent special differentiation structures.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Sep;357(3):645-65. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1906-9. Epub 2014 Jun 8. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 24907851 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-testis barrier: a review on regulators in maintaining cell junction integrity between Sertoli cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 May;396(2):157-175. doi: 10.1007/s00441-024-03894-7. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 38564020 Review.
References
-
- Abraham RT, Wiederrecht GJ. Immunopharmacology of rapamycin. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:483–510. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr. Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Aliabadi AZ, Pohanka E, Seebacher G, Dunkler D, Kammerstatter D, Wolner E, Grimm M, Zuckermann AO. Development of proteinuria after switch to sirolimus- based immunosuppression in long-term cardiac transplant patients. Am J. Transplant. 2008;8:854–861. - PubMed
-
- Amato R, D’Antona L, Porciatti G, Agosti V, Menniti M, Rinaldo C, Costa N, Bellacchio E, Mattarocci S, Fuiano G, et al. Sgk1 activates MDM2-dependent p53 degradation and affects cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 2009;87:1221–1239. - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucoq JM, Hemmings BA. Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase. B.J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:31515–31524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

