Effect of repeated exposure to MDMA on the function of the 5-HT transporter as assessed by synaptosomal 5-HT uptake
- PMID: 23318273
- PMCID: PMC3578032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.01.003
Effect of repeated exposure to MDMA on the function of the 5-HT transporter as assessed by synaptosomal 5-HT uptake
Abstract
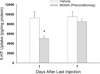
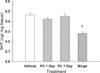
Recent studies have demonstrated that a preconditioning regimen (i.e., repeated low doses) of MDMA provides protection against the reductions in tissue concentrations of 5-HT and 5-HT transporter (SERT) density and/or expression produced by a subsequent binge regimen of MDMA. In the present study, the effects of preconditioning and binge treatment regimens of MDMA on SERT function were assessed by synaptosomal 5-HT uptake. Synaptosomal 5-HT uptake was reduced by 72% 7 days following the binge regimen (10 mg/kg, i.p. every 2 h for a total of 4 injections). In rats exposed to the preconditioning regimen of MDMA (daily treatment with 10 mg/kg for 4 days), the reduction in synaptosomal 5-HT uptake induced by a subsequent binge regimen was significantly less. Treatment with the preconditioning regimen alone resulted in a transient 46% reduction in 5-HT uptake that was evident 1 day, but not 7 days, following the last injection of MDMA. Furthermore, the preconditioning regimen of MDMA did not alter tissue concentrations of 5-HT, whereas the binge regimen of MDMA resulted in a long-term reduction of 40% of tissue 5-HT concentrations. The distribution of SERT immunoreactivity (ir) in membrane and endosomal fractions of the hippocampus also was evaluated following the preconditioning regimen of MDMA. There was no significant difference in the relative distribution of SERTir between these two compartments in control and preconditioned rats. The results demonstrate that SERT function is transiently reduced in response to a preconditioning regimen of MDMA, while long-term reductions in SERT function occur in response to a binge regimen of MDMA. Moreover, a preconditioning regimen of MDMA provides protection against the long-term reductions in SERT function evoked by a subsequent binge regimen of the drug. It is tempting to speculate that the neuroprotective effect of MDMA preconditioning results from a transient down-regulation in SERT function.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Repeated exposure to MDMA provides neuroprotection against subsequent MDMA-induced serotonin depletion in brain.Brain Res. 2009 Aug 25;1286:32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.06.042. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19555677 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced 5-HT depletion by the administration of L-5-hydroxytryptophan.Neuroscience. 2007 Aug 10;148(1):212-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.024. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17629409
-
Repeated administration of the substituted amphetamine p-methoxyamphetamine produces reductions in cortical 5-HT transporter binding but not 5-HT content, unlike 3,4-methylenedioxyamethamphetamine.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 28;546(1-3):74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.07.011. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16925993
-
The effects of ecstasy on neurotransmitter systems: a review on the findings of molecular imaging studies.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Oct;233(19-20):3473-501. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4396-5. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27568200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin transporter availability, neurocognitive function and their correlation in abstinent 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine users.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2022 Jan;37(1):e2811. doi: 10.1002/hup.2811. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34506649 Review.
Cited by
-
Striatal serotonin transporter gain-of-function in L-DOPA-treated, hemi-parkinsonian rats.Brain Res. 2023 Jul 15;1811:148381. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148381. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 37127174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguirre N, Ballaz S, Lasheras B, Del Rio J. MDMA ('Ecstasy') enhances 5-HT1A receptor density and 8-OH-DPAT-induced hypothermia: blockade by drugs preventing 5-hydroxytryptamine depletion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998;346:181–188. - PubMed
-
- Asano S, Matsuda T, Nakasu Y, Maeda S, Nogi H, Baba A. Inhibition by nitric oxide of the uptake of [3H]serotonin into rat brain synaptosomes. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1997;75:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Yeh SY, O'Hearn E, Molliver ME, Kuhar MJ, De Souza EB. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine destroy serotonin terminals in rat brain: quantification of neurodegeneration by measurement of [3H]paroxetine-labeled serotonin uptake sites. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987;242:911–916. - PubMed
-
- Biezonski DK, Meyer JS. Effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on serotonin transporter and vesicular monoamine transporter 2 protein and gene expression in rats: implications for MDMA neurotoxicity. J. Neurochem. 2010;112:951–962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

