The ARF tumor-suppressor controls Drosha translation to prevent Ras-driven transformation
- PMID: 23318441
- PMCID: PMC3934099
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.601
The ARF tumor-suppressor controls Drosha translation to prevent Ras-driven transformation
Abstract
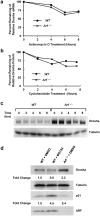
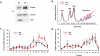
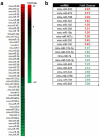
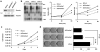
ARF is a multifunctional tumor suppressor that acts as both a sensor of oncogenic stimuli and as a key regulator of ribosome biogenesis. Recently, our group established the DEAD-box RNA helicase and microRNA (miRNA) microprocessor accessory subunit, DDX5, as a critical target of basal ARF function. To identify other molecular targets of ARF, we focused on known interacting proteins of DDX5 in the microprocessor complex. Drosha, the catalytic core of the microprocessor complex, has a critical role in the maturation of specific non-coding RNAs, including miRNAs and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs). Here, we report that chronic or acute loss of Arf enhanced Drosha protein expression. This induction did not involve Drosha mRNA transcription or protein stability but rather relied on the increased translation of existing Drosha mRNAs. Enhanced Drosha expression did not alter global miRNA production but rather modified expression of a subset of miRNAs in the absence of Arf. Elevated Drosha protein levels were required to maintain the increased rRNA synthesis and cellular proliferation observed in the absence of Arf. Arf-deficient cells transformed by oncogenic Ras(V12) were dependent on increased Drosha expression as Drosha knockdown was sufficient to inhibit Ras-dependent cellular transformation. Thus, we propose that ARF regulates Drosha mRNA translation to prevent aberrant cell proliferation and Ras-dependent transformation.
Figures
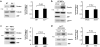
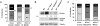

References
-
- Quelle DE, Zindy F, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ. Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell. 1995;83:993–1000. - PubMed
-
- Weber JD, Taylor LJ, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Bar-Sagi D. Nucleolar Arf sequesters Mdm2 and activates p53. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:20–26. - PubMed
-
- Pomerantz J, Schreiber-Agus N, Liegeois NJ, Silverman A, Alland L, Chin L, et al. The Ink4a tumor suppressor gene product, p19Arf, interacts with MDM2 and neutralizes MDM2's inhibition of p53. Cell. 1998;92:713–723. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Yarbrough WG. ARF promotes MDM2 degradation and stabilizes p53: ARF-INK4a locus deletion impairs both the Rb and p53 tumor suppression pathways. Cell. 1998;92:725–734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

