NG2-cells are not the cell of origin for murine neurofibromatosis-1 (Nf1) optic glioma
- PMID: 23318450
- PMCID: PMC3874418
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.580
NG2-cells are not the cell of origin for murine neurofibromatosis-1 (Nf1) optic glioma
Abstract
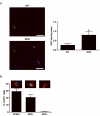
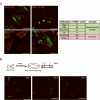
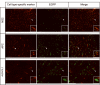
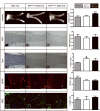
Low-grade glial neoplasms (astrocytomas) represent one of the most common brain tumors in the pediatric population. These tumors frequently form in the optic pathway (optic pathway gliomas, OPGs), especially in children with the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-inherited tumor predisposition syndrome. To model these tumors in mice, we have previously developed several Nf1 genetically-engineered mouse strains that form optic gliomas. However, there are three distinct macroglial cell populations in the optic nerve (astrocytes, NG2+ (nerve/glial antigen 2) cells and oligodendrocytes). The presence of NG2+ cells in the optic nerve raises the intriguing possibility that these cells could be the tumor-initiating cells, as has been suggested for adult glioma. In this report, we used a combination of complementary in vitro and novel genetically-engineered mouse strains in vivo to determine whether NG2+ cells could give rise to Nf1 optic glioma. First, we show that Nf1 inactivation results in a cell-autonomous increase in glial fibrillary acidic protein+ (GFAP+), but not in NG2+, cell proliferation in vitro. Second, similar to the GFAP-Cre transgenic strain that drives Nf1 optic gliomagenesis, NG2-expressing cells also give rise to all three macroglial lineages in vivo. Third, in contrast to the GFAP-Cre strain, Nf1 gene inactivation in NG2+ cells is not sufficient for optic gliomagenesis in vivo. Collectively, these data demonstrate that NG2+ cells are not the cell of origin for mouse optic glioma, and support a model in which gliomagenesis requires Nf1 loss in specific neuroglial progenitors during embryogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Blazo MA, Lewis RA, Chintagumpala MM, Frazier M, McCluggage C, Plon SE. Outcomes of systematic screening for optic pathway tumors in children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Am J Med Genet A. 2004 Jun 15;127A(3):224–9. - PubMed
-
- Lund AM, Skovby F. Optic gliomas in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Oct;150(12):835–8. - PubMed
-
- Listernick R, Darling C, Greenwald M, Strauss L, Charrow J. Optic pathway tumors in children: the effect of neurofibromatosis type 1 on clinical manifestations and natural history. J Pediatr. 1995 Nov;127(5):718–22. - PubMed
-
- Czyzyk E, Jozwiak S, Roszkowski M, Schwartz RA. Optic pathway gliomas in children with and without neurofibromatosis 1. J Child Neurol. 2003 Jul;18(7):471–8. - PubMed
-
- Listernick R, Louis DN, Packer RJ, Gutmann DH. Optic pathway gliomas in children with neurofibromatosis 1: consensus statement from the NF1 Optic Pathway Glioma Task Force. Ann Neurol. 1997 Feb;41(2):143–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

