Circadian clock-controlled diurnal oscillation of Ras/ERK signaling in mouse liver
- PMID: 23318682
- PMCID: PMC3611956
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.89.59
Circadian clock-controlled diurnal oscillation of Ras/ERK signaling in mouse liver
Abstract
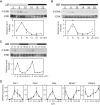
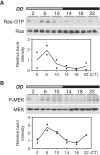
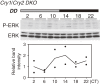
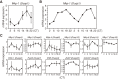
Accumulating evidence indicates that ERK MAP kinase signaling plays an important role in the regulation of the circadian clock, especially in the clock-resetting mechanism in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in mammals. Previous studies have also shown that ERK phosphorylation exhibits diurnal variation in the SCN. However, little is known about circadian regulation of ERK signaling in peripheral tissues. Here we show that the activity of Ras/ERK signaling exhibits circadian rhythms in mouse liver. We demonstrate that Ras activation, MEK phosphorylation, and ERK phosphorylation oscillate in a circadian manner. As the oscillation of ERK phosphorylation is lost in Cry1/Cry2 double-knockout mice, Ras/ERK signaling should be under the control of the circadian clock. Furthermore, expression of MAP kinase phosphatase-1 (Mkp-1) shows diurnal changes in liver. These results indicate that Ras/ERK signaling is strictly regulated by the circadian clock in liver, and suggest that the circadian oscillation of the activities of Ras, MEK, and ERK may regulate diurnal variation of liver function and/or homeostasis.(Communicated by Shigekazu NAGATA, M.J.A.).
Figures
References
-
- Reppert S.M., Weaver D.R. (2002) Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature 418, 935–941 - PubMed
-
- Ko C.H., Takahashi J.S. (2006) Molecular components of the mammalian circadian clock. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, R271–R277 - PubMed
-
- Hastings M.H., Reddy A.B., Maywood E.S. (2003) A clockwork web: circadian timing in brain and periphery, in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 649–661 - PubMed
-
- Gachon F., Olela F.F., Schaad O., Descombes P., Schibler U. (2006) The circadian PAR-domain basic leucine zipper transcription factors DBP, TEF, and HLF modulate basal and inducible xenobiotic detoxification. Cell Metab. 4, 25–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

