Gene-microRNA interactions associated with antipsychotic mechanisms and the metabolic side effects of olanzapine
- PMID: 23318695
- PMCID: PMC3622003
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-012-2939-y
Gene-microRNA interactions associated with antipsychotic mechanisms and the metabolic side effects of olanzapine
Abstract
Rationale: Changes in the cortical expression of small non-coding microRNA (miRNA) have been observed in postmortem analysis of psychotic disorders. Antipsychotic drugs (APDs) are the most effective treatment option for these disorders and have been associated with changes in gene expression. MicroRNA regulate numerous genes involved in brain development and function. It is therefore plausible to question whether miRNA expression is also altered and hence whether they take part in the neuroleptic mechanism of action.
Objectives: We sought to investigate whether treatment with APDs induces changes in miRNA expression and query the functional implications of such changes. Furthermore, we investigated the possible functional interplay of miRNA-gene regulatory interactions.
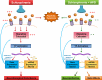
Method: High-throughput miRNA profiling of the whole brain of C57BL/6 mice treated with haloperidol, olanzapine or clozapine for 7 days was performed. Functional analysis was conducted on the putative targets of altered microRNA. Significant miRNA-gene regulatory interactions were evaluated by the integration of genome-wide mRNA expression analysis using the Bayesian networks with splitting-averaging strategy and functional analysis conducted.
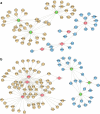
Results: Small subsets of miRNA were altered with each treatment with potential neurologically relevant influence. Metabolic pathways were enriched in olanzapine and clozapine treatments, possibly associated with their weight gain side effects. Neurologically and metabolically relevant miRNA-gene interaction networks were identified in the olanzapine treatment group.
Conclusion: This study is the first to suggest a role for miRNA in the mechanism of APD action and the metabolic side effects of the atypical ADPs, and adds support for their consideration in pharmacogenomics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coregulation of genes in the mouse brain following treatment with clozapine, haloperidol, or olanzapine implicates altered potassium channel subunit expression in the mechanism of antipsychotic drug action.Psychiatr Genet. 2008 Oct;18(5):226-39. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e3283053019. Psychiatr Genet. 2008. PMID: 18797397
-
[Antipsychotics in bipolar disorders].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):417-24. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95456-5. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627046 Review. French.
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
-
Antipsychotic drug-associated gene-miRNA interaction in T-lymphocytes.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Jun;17(6):929-43. doi: 10.1017/S1461145713001752. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24480591
-
Effects of haloperidol, clozapine and olanzapine on the survival of human neuronal and immune cells in vitro.J Psychopharmacol. 2007 Nov;21(8):851-6. doi: 10.1177/0269881107077221. Epub 2007 Sep 19. J Psychopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17881431
Cited by
-
Haloperidol induces pharmacoepigenetic response by modulating miRNA expression, global DNA methylation and expression profiles of methylation maintenance genes and genes involved in neurotransmission in neuronal cells.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 8;12(9):e0184209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184209. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28886082 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of microRNA in Schizophrenia: A Scoping Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7673. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147673. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062916 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of microRNAs in neuropsychiatric disorders: Past, present, and future.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Feb 6;73:87-103. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27072377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship between 10 Years Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Schizophrenia Symptoms: Preliminary Results.Psychiatry Investig. 2019 Dec;16(12):933-939. doi: 10.30773/pi.2019.0063. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Psychiatry Investig. 2019. PMID: 31801314 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA's impact on neurotransmitter and neuropeptide systems: small but mighty mediators of anxiety.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Jun;468(6):1061-9. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1814-9. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 27138168 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

