Repeated in vivo exposure of cocaine induces long-lasting synaptic plasticity in hypocretin/orexin-producing neurons in the lateral hypothalamus in mice
- PMID: 23318871
- PMCID: PMC3624862
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.246983
Repeated in vivo exposure of cocaine induces long-lasting synaptic plasticity in hypocretin/orexin-producing neurons in the lateral hypothalamus in mice
Abstract
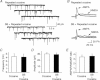
Hypocretin (orexin), a neuropeptide synthesized exclusively in the perifornical/lateral hypothalamus, is critical for drug seeking and relapse, but it is not clear how the circuitry centred on hypocretin-producing neurons (hypocretin neurons) is modified by drugs of abuse and how changes in this circuit might alter behaviours related to drug addiction. In this study, we show that repeated, but not single, in vivo cocaine administration leads to a long-lasting, experience-dependent potentiation of glutamatergic synapses on hypocretin neurons in mice following a cocaine-conditioned place preference (CPP) protocol. The synaptic potentiation occurs postsynaptically and probably involves up-regulation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors on hypocretin neurons. Phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) is also significantly increased in hypocretin neurons in cocaine-treated animals, suggesting that CREB-mediated pathways may contribute to synaptic potentiation in these cells. Furthermore, the potentiation of synaptic efficacy in hypocretin neurons persists during cocaine withdrawal, but reverses to baseline levels after prolonged abstinence. Finally, the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) triggered by a high-frequency stimulation is facilitated in hypocretin neurons in cocaine-treated mice, suggesting that long-lasting changes in synapses onto hypocretin neurons would probably be further potentiated by other stimuli (such as concurrent environmental cues) paired with the drug. In summary, we show here that hypocretin neurons undergo experience-dependent synaptic potentiation that is distinct from that reported in other reward systems, such as the ventral tegmental area, following exposure to cocaine. These findings support the idea that the hypocretin system is important for behavioural changes associated with cocaine administration in animals and humans.
Figures





References
-
- Adams WJ, Lorens SA, Mitchell CL. Morphine enhances lateral hypothalamic self-stimulation in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972;140:770–771. - PubMed
-
- Badiani A, Robinson TE. Drug-induced neurobehavioral plasticity: the role of environmental context. Behav Pharmacol. 2004;15:327–339. - PubMed
-
- Balcita-Pedicino JJ, Sesack SR. Orexin axons in the rat ventral tegmental area synapse infrequently onto dopamine and γ-aminobutyric acid neurons. J Comp Neurol. 2007;503:668–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

