Finite element analysis of the pelvis after modular hemipelvic endoprosthesis reconstruction
- PMID: 23318936
- PMCID: PMC3609974
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-012-1756-6
Finite element analysis of the pelvis after modular hemipelvic endoprosthesis reconstruction
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the biomechanics of the pelvis reconstructed with a modular hemipelvic prosthesis using finite element (FE) analysis.
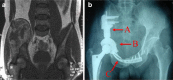
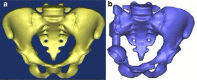
Methods: A three-dimensional FE model of the postoperative pelvis was developed and input into the Abaqus FEA software version 6.7.1. Mesh refinement tests were then performed and a force of 500 N was applied at the lamina terminalis of the fifth lumbar vertebra along the longitudinal axis of the normal pelvis and the postoperative pelvis for three positions: sitting, standing on two feet, and standing on the foot of the affected side. Stress distribution analysis was performed between the normal pelvis and postoperative pelvis at these three static positions.
Results: In the normal pelvis, stress distribution was concentrated on the superior area of the acetabulum, arcuate line, sacroiliac joint, sacral midline and, in particular, the superior area of the greater sciatic notch. In the affected postoperative hemipelvis, stress distribution was concentrated on the proximal area of the pubic plate, the top of the acetabular cup, the connection between the CS-fixator and acetabular cup and the fixation between the prosthesis and sacroiliac joint.
Conclusions: Stress distribution of the postoperative pelvis was similar to the normal pelvis at three different static positions. Reconstruction with a modular hemipelvic prosthesis yielded good biomechanical characteristics.
Figures




Comment in
-
Finite element analysis of the pelvis after modular hemipelvic endoprosthesis reconstruction.Int Orthop. 2013 Oct;37(10):2097-8. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-1973-7. Int Orthop. 2013. PMID: 23797456 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bell RS, Davis AM, Wunder JS, Buconjic T, McGoveran B, Gross AE. Allograft reconstruction of the acetabulum after resection of grade II B sarcoma. Intermediate term results. J Bone Joint Surg. 1997;79A:1663–1674. - PubMed
-
- Harrington KD. The use of hemipelvis allografts or autoclaved grafts for reconstruction after wide resection of malignant tumors of the pelvis. J Bone Joint Surg. 1992;74:331–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

