The QKI-5 and QKI-6 RNA binding proteins regulate the expression of microRNA 7 in glial cells
- PMID: 23319046
- PMCID: PMC3592017
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01604-12
The QKI-5 and QKI-6 RNA binding proteins regulate the expression of microRNA 7 in glial cells
Abstract
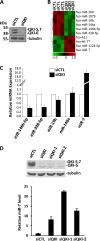
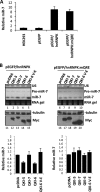
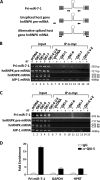
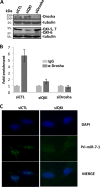
The quaking (qkI) gene encodes 3 major alternatively spliced isoforms that contain unique sequences at their C termini dictating their cellular localization. QKI-5 is predominantly nuclear, whereas QKI-6 is distributed throughout the cell and QKI-7 is cytoplasmic. The QKI isoforms are sequence-specific RNA binding proteins expressed mainly in glial cells modulating RNA splicing, export, and stability. Herein, we identify a new role for the QKI proteins in the regulation of microRNA (miRNA) processing. We observed that small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated QKI depletion of U343 glioblastoma cells leads to a robust increase in miR-7 expression. The processing from primary to mature miR-7 was inhibited in the presence QKI-5 and QKI-6 but not QKI-7, suggesting that the nuclear localization plays an important role in the regulation of miR-7 expression. The primary miR-7-1 was bound by the QKI isoforms in a QKI response element (QRE)-specific manner. We observed that the pri-miR-7-1 RNA was tightly bound to Drosha in the presence of the QKI isoforms, and this association was not observed in siRNA-mediated QKI or Drosha-depleted U343 glioblastoma cells. Moreover, the presence of the QKI isoforms led to an increase presence of pri-miR-7 in nuclear foci, suggesting that pri-miR-7-1 is retained in the nucleus by the QKI isoforms. miR-7 is known to target the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR) 3' untranslated region (3'-UTR), and indeed, QKI-deficient U343 cells had reduced EGFR expression and decreased ERK activation in response to EGF. Elevated levels of miR-7 are associated with cell cycle arrest, and it was observed that QKI-deficient U343 that harbor elevated levels of miR-7 exhibited defects in cell proliferation that were partially rescued by the addition of a miR-7 inhibitor. These findings suggest that the QKI isoforms regulate glial cell function and proliferation by regulating the processing of certain miRNAs.
Figures


References
-
- van Kouwenhove M, Kedde M, Agami R. 2011. MicroRNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins and its implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11:644–656 - PubMed
-
- Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ. 2004. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 432:231–235 - PubMed
-
- Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R. 2004. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 432:235–240 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
