Identification and cytoprotective function of a novel nestin isoform, Nes-S, in dorsal root ganglia neurons
- PMID: 23319587
- PMCID: PMC3605656
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.408179
Identification and cytoprotective function of a novel nestin isoform, Nes-S, in dorsal root ganglia neurons
Abstract
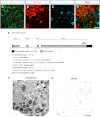
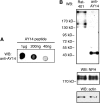
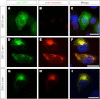
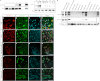
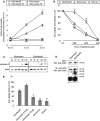
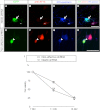
In this study, the first nestin isoform, Nes-S, was identified in neurons of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of adult rats. Nes-S cannot form filaments by itself in cytoplasmic intermediate filament-free SW13 cells. Instead, it co-assembles into filaments with vimentin when transfected into vimentin(+) SW13 cells, and with peripherin and neurofilament proteins when transfected into N2a cells. In primary DRG neurons, endogenous Nes-S co-assembles with peripherin and neurofilament proteins. The expression of Nes-S first appears in DRG at postnatal day 5 and persists to adulthood. Among the adult tissues we examined, the expression of Nes-S is restricted to the sensory and motor neurons. Finally, exogenous Nes-S enhances viability when transfected into N2a cells, and knockdown of endogenous Nes-S impairs the survival of DRG neurons in primary cultures. Taken together, Nes-S is a new neuronal intermediate filament protein that exerts a cytoprotective function in mature sensory and motor neurons.
Figures


References
-
- Lendahl U., Zimmerman L. B., McKay R. D. (1990) CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell 60, 585–595 - PubMed
-
- Yang H. Y., Lieska N., Goldman A. E., Goldman R. D. (1992) Colchicine-sensitive and colchicine-insensitive intermediate filament systems distinguished by a new intermediate filament-associated protein, IFAP-70/280 kD. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 22, 185–199 - PubMed
-
- Steinert P. M., Chou Y. H., Prahlad V., Parry D. A., Marekov L. N., Wu K. C., Jang S. I., Goldman R. D. (1999) A high molecular weight intermediate filament-associated protein in BHK-21 cells is nestin, a type VI intermediate filament protein: limited co-assembly in vitro to form heteropolymers with type III vimentin and type IV α-internexin. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 9881–9890 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

