The MLK-related kinase (MRK) is a novel RhoC effector that mediates lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-stimulated tumor cell invasion
- PMID: 23319595
- PMCID: PMC3581392
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.414060
The MLK-related kinase (MRK) is a novel RhoC effector that mediates lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-stimulated tumor cell invasion
Abstract
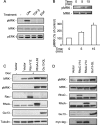
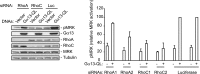
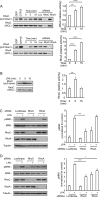
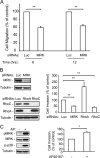
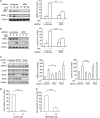
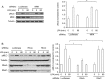
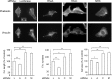
The small GTPase RhoC is overexpressed in many invasive tumors and is essential for metastasis. Despite its high structural homology to RhoA, RhoC appears to perform functions that are different from those controlled by RhoA. The identity of the signaling components that are differentially regulated by these two GTPases is only beginning to emerge. Here, we show that the MAP3K protein MRK directly binds to the GTP-bound forms of both RhoA and RhoC in vitro. However, siRNA-mediated depletion of MRK in cells phenocopies depletion of RhoC, rather than that of RhoA. MRK depletion, like that of RhoC, inhibits LPA-stimulated cell invasion, while depletion of RhoA increases invasion. We also show that active MRK enhances LPA-stimulated invasion, further supporting a role for MRK in the regulation of invasion. Depletion of either RhoC or MRK causes sustained myosin light chain phosphorylation after LPA stimulation. In addition, activation of MRK causes a reduction in myosin light chain phosphorylation. In contrast, as expected, depletion of RhoA inhibits myosin light chain phosphorylation. We also present evidence that both RhoC and MRK are required for LPA-induced stimulation of the p38 and ERK MAP kinases. In conclusion, we have identified MRK as a novel RhoC effector that controls LPA-stimulated cell invasion at least in part by regulating myosin dynamics, ERK and p38.
Figures


References
-
- Sahai E., Marshall C. J. (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 133–142 - PubMed
-
- Karlsson R., Pedersen E. D., Wang Z., Brakebusch C. (2009) Rho GTPase function in tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1796, 91–98 - PubMed
-
- Kamai T., Arai K., Tsujii T., Honda M., Yoshida K. (2001) Overexpression of RhoA mRNA is associated with advanced stage in testicular germ cell tumour. BJU. Int. 87, 227–231 - PubMed
-
- van Golen K. L., Davies S., Wu Z. F., Wang Y., Bucana C. D., Root H., Chandrasekharappa S., Strawderman M., Ethier S. P., Merajver S. D. (1999) A novel putative low-affinity insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, LIBC (lost in inflammatory breast cancer), and RhoC GTPase correlate with the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Clin. Cancer Res. 5, 2511–2519 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

