Delicate balance among three types of T cells in concurrent regulation of tumor immunity
- PMID: 23319803
- PMCID: PMC3622595
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2567
Delicate balance among three types of T cells in concurrent regulation of tumor immunity
Abstract
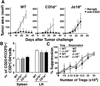
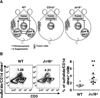
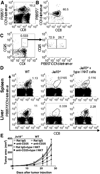
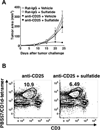
The nature of the regulatory cell types that dominate in any given tumor is not understood at present. Here, we addressed this question for regulatory T cells (Treg) and type II natural killer T (NKT) cells in syngeneic models of colorectal and renal cancer. In mice with both type I and II NKT cells, or in mice with neither type of NKT cell, Treg depletion was sufficient to protect against tumor outgrowth. Surprisingly, in mice lacking only type I NKT cells, Treg blockade was insufficient for protection. Thus, we hypothesized that type II NKT cells may be neutralized by type I NKT cells, leaving Tregs as the primary suppressor, whereas in mice lacking type I NKT cells, unopposed type II NKT cells could suppress tumor immunity even when Tregs were blocked. We confirmed this hypothesis in 3 ways by reconstituting type I NKT cells as well as selectively blocking or activating type II NKT cells with antibody or the agonist sulfatide, respectively. In this manner, we showed that blockade of both type II NKT cells and Tregs is necessary to abrogate suppression of tumor immunity, but a third cell, the type I NKT cell, determines the balance between these regulatory mechanisms. As patients with cancer often have deficient type I NKT cell function, managing this delicate balance among 3 T-cell subsets may be critical for the success of immunotherapy for human cancer.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tissue-Specific Roles of NKT Cells in Tumor Immunity.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 15;9:1838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01838. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30158927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfatide-activated type II NKT cells suppress immunogenic maturation of lung dendritic cells in murine models of asthma.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):L578-L590. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00256.2018. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31432714
-
Cross-regulation between type I and type II NKT cells in regulating tumor immunity: a new immunoregulatory axis.J Immunol. 2007 Oct 15;179(8):5126-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5126. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17911598
-
Host natural killer T cells induce an interleukin-4-dependent expansion of donor CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells that protects against graft-versus-host disease.Blood. 2009 Apr 30;113(18):4458-67. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-165506. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19221040 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-regulation between distinct natural killer T cell subsets influences immune response to self and foreign antigens.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Feb;218(2):246-50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21597. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18814145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Japanese Kampo Medicine Juzentaihoto Improves Antiviral Cellular Immunity in Tumour-Bearing Hosts.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 13;2022:6122955. doi: 10.1155/2022/6122955. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35996405 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on the tumor immune microenvironment in gastrointestinal tumors.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 8;12:1054598. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1054598. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of Tissue-Resident Invariant NKT Cells by Vitamin A Metabolites and P2X7-Mediated Cell Death.J Immunol. 2019 Sep 1;203(5):1189-1197. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900398. Epub 2019 Jul 15. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31308092 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofibromin 1 Impairs Natural Killer T-Cell-Dependent Antitumor Immunity against a T-Cell Lymphoma.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 5;8:1901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01901. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29354122 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Implantation-Based Genetic Modeling of Biliary Carcinogenesis in Mice.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 11;13(10):2292. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102292. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064809 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:329–360. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa H, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells in tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:759–767. - PubMed
-
- Nagaraj S, Gabrilovich DI. Tumor escape mechanism governed by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2561–2563. - PubMed
-
- Terabe M, Berzofsky JA. NKT cells in immunoregulation of tumor immunity: a new immunoregulatory axis. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:491–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

